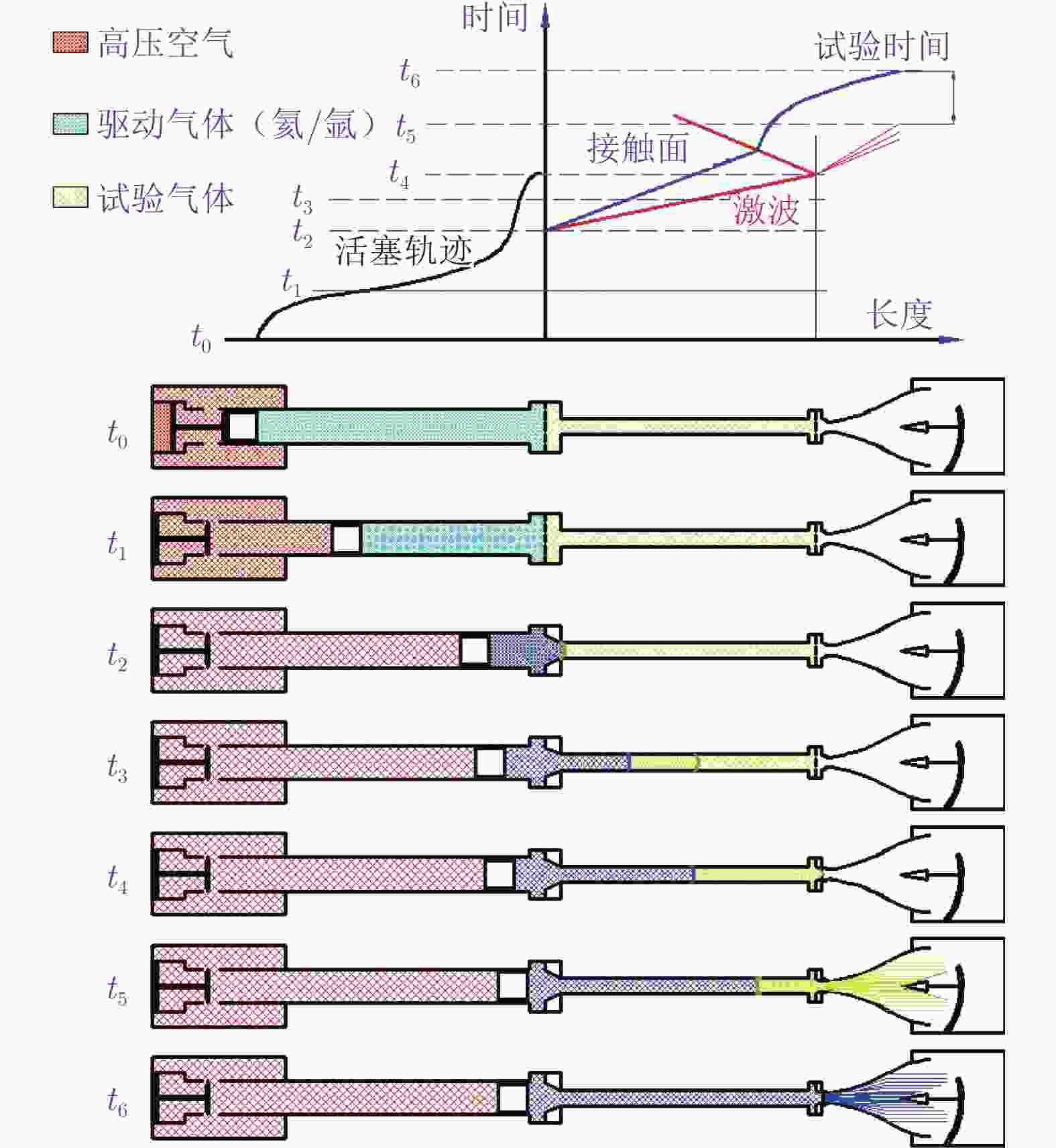
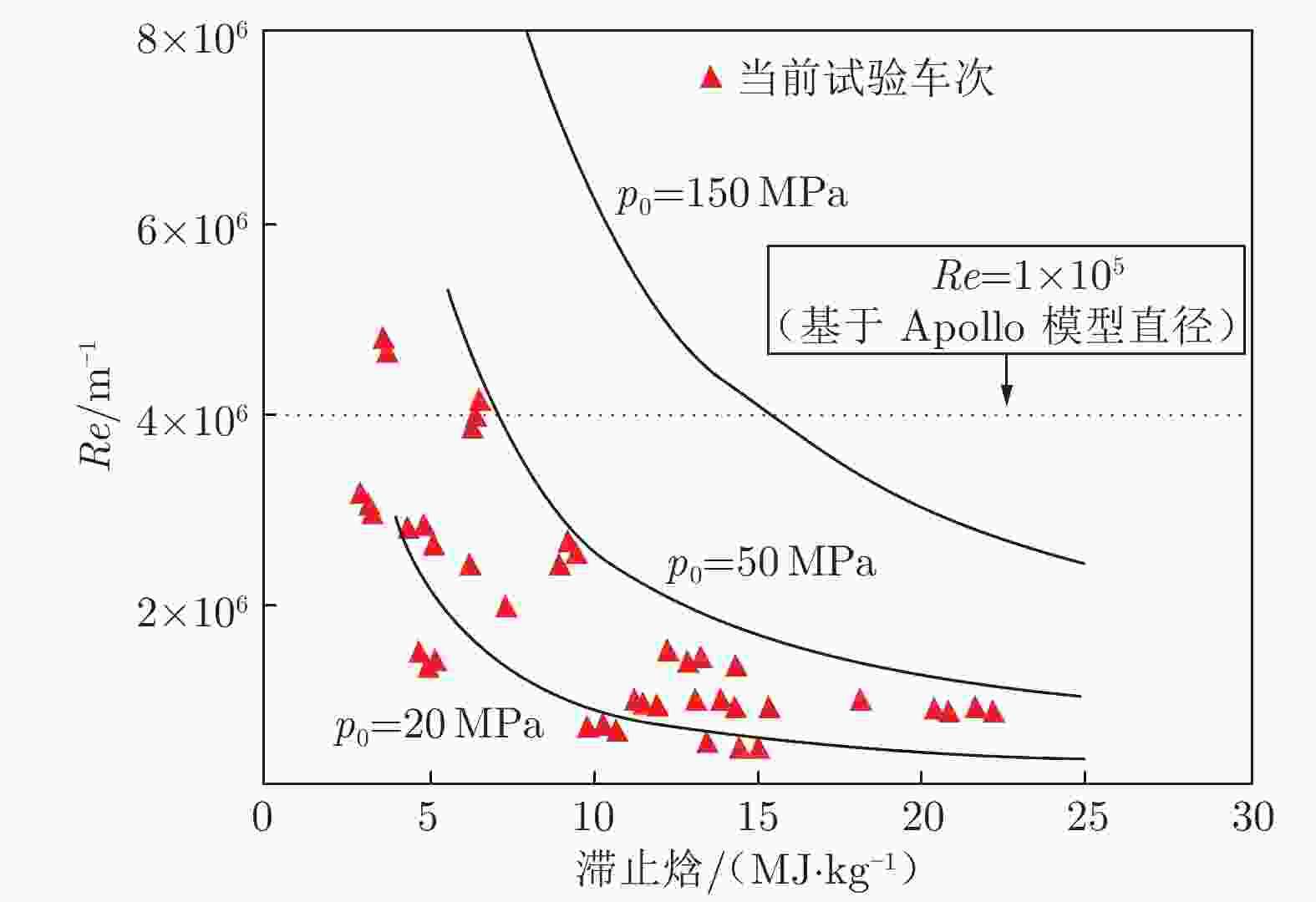
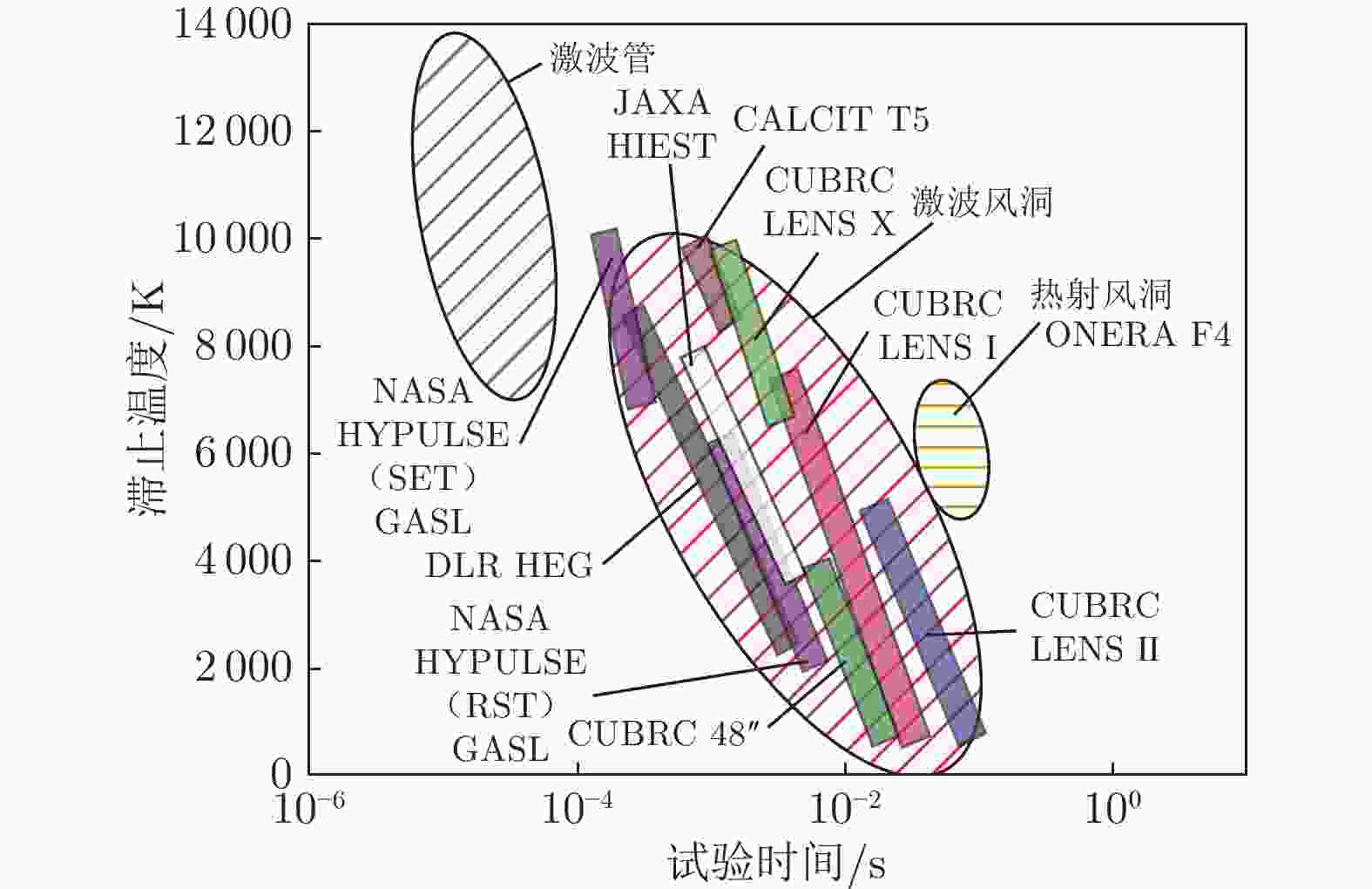
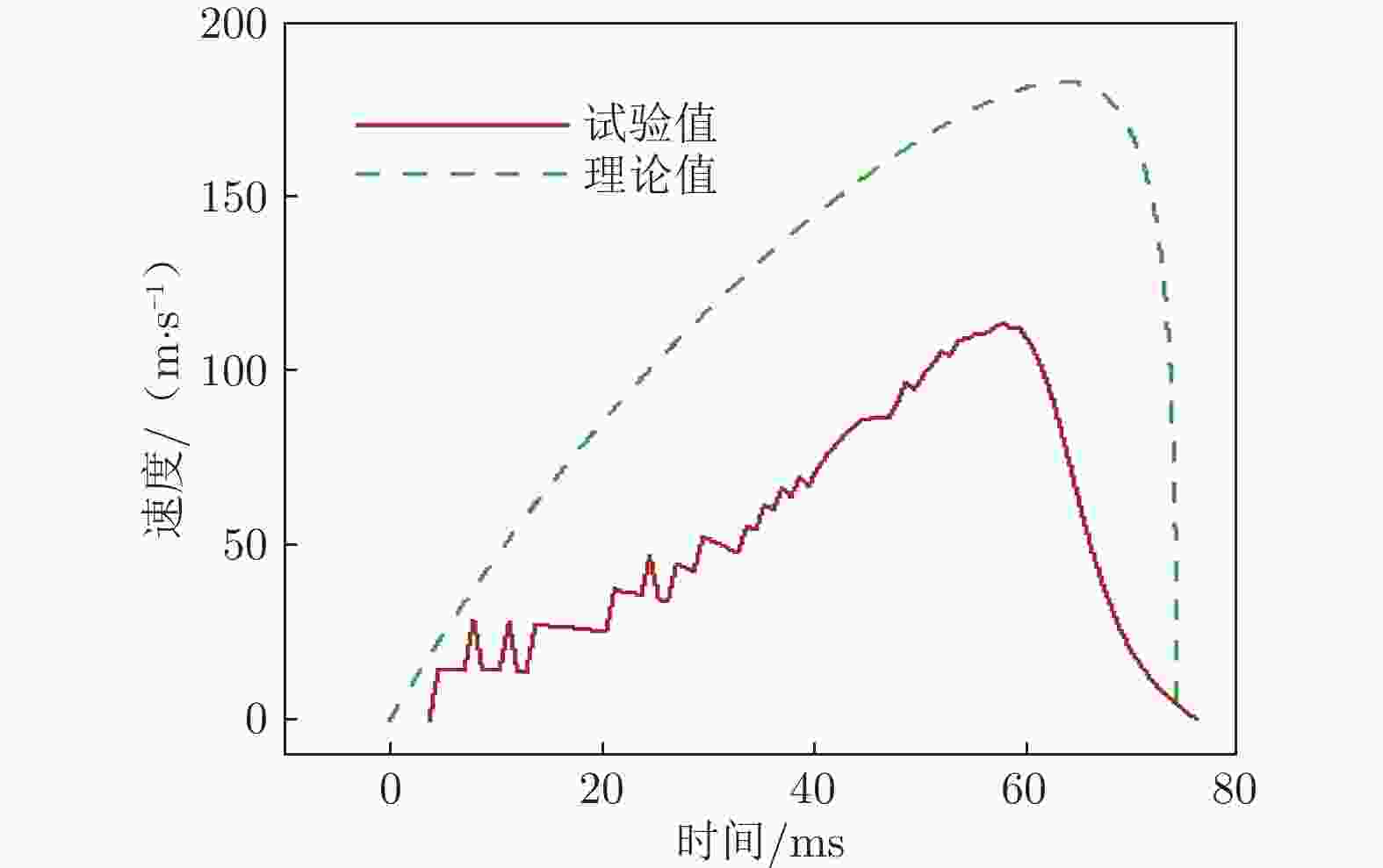
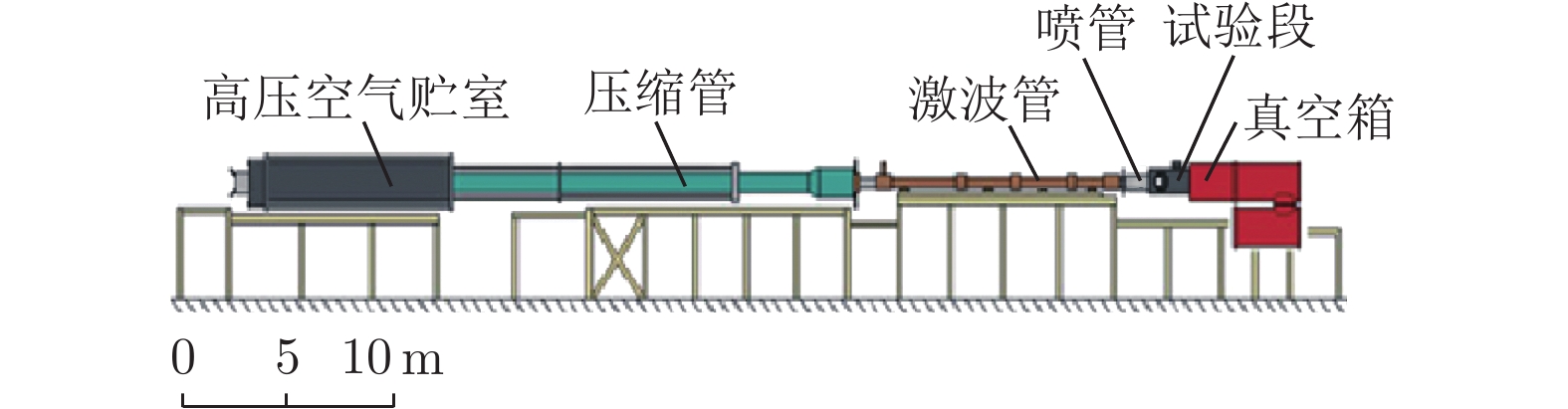
The development and key technologies of 2.0 m high energy shock tunnel
-
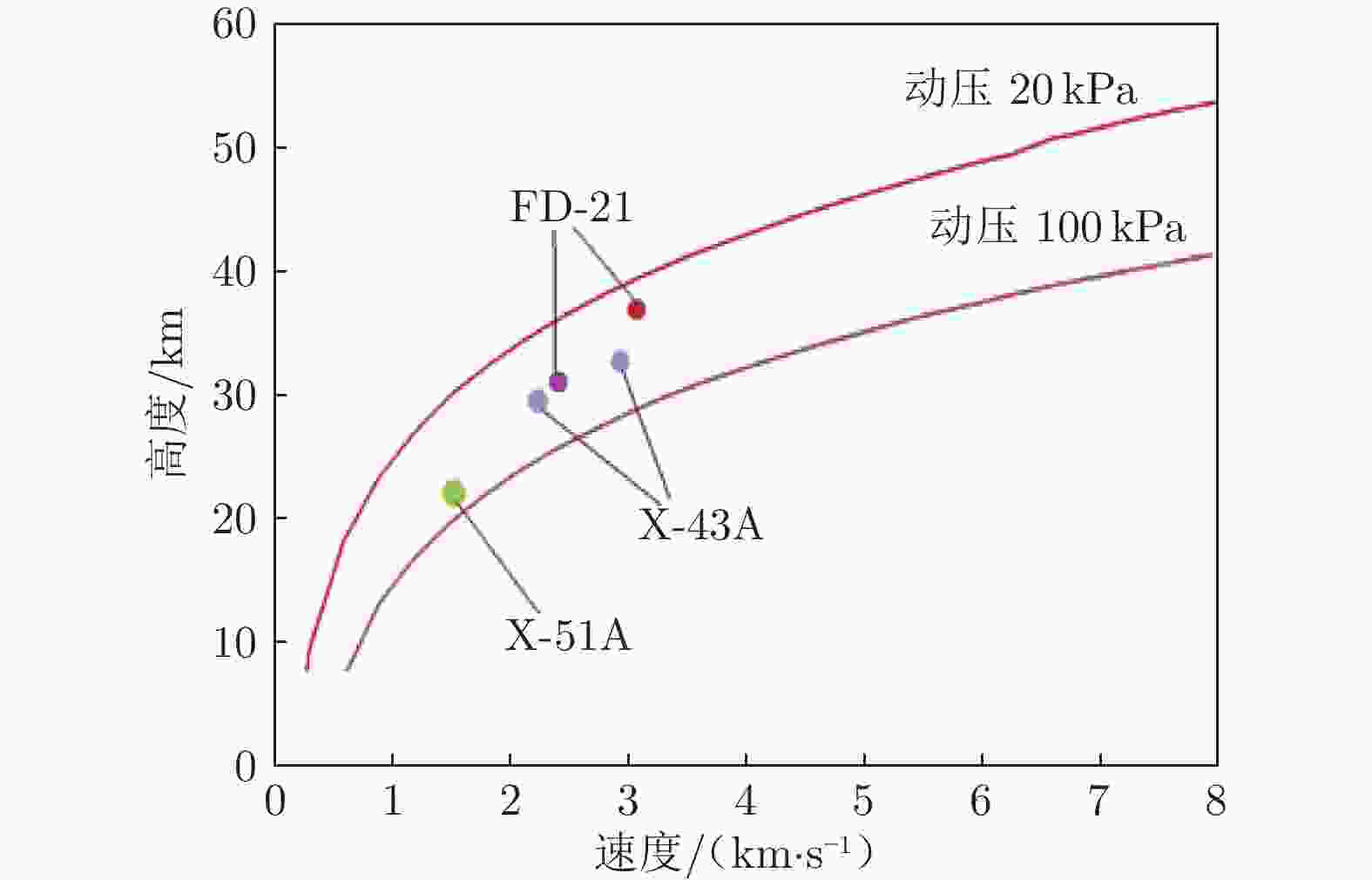
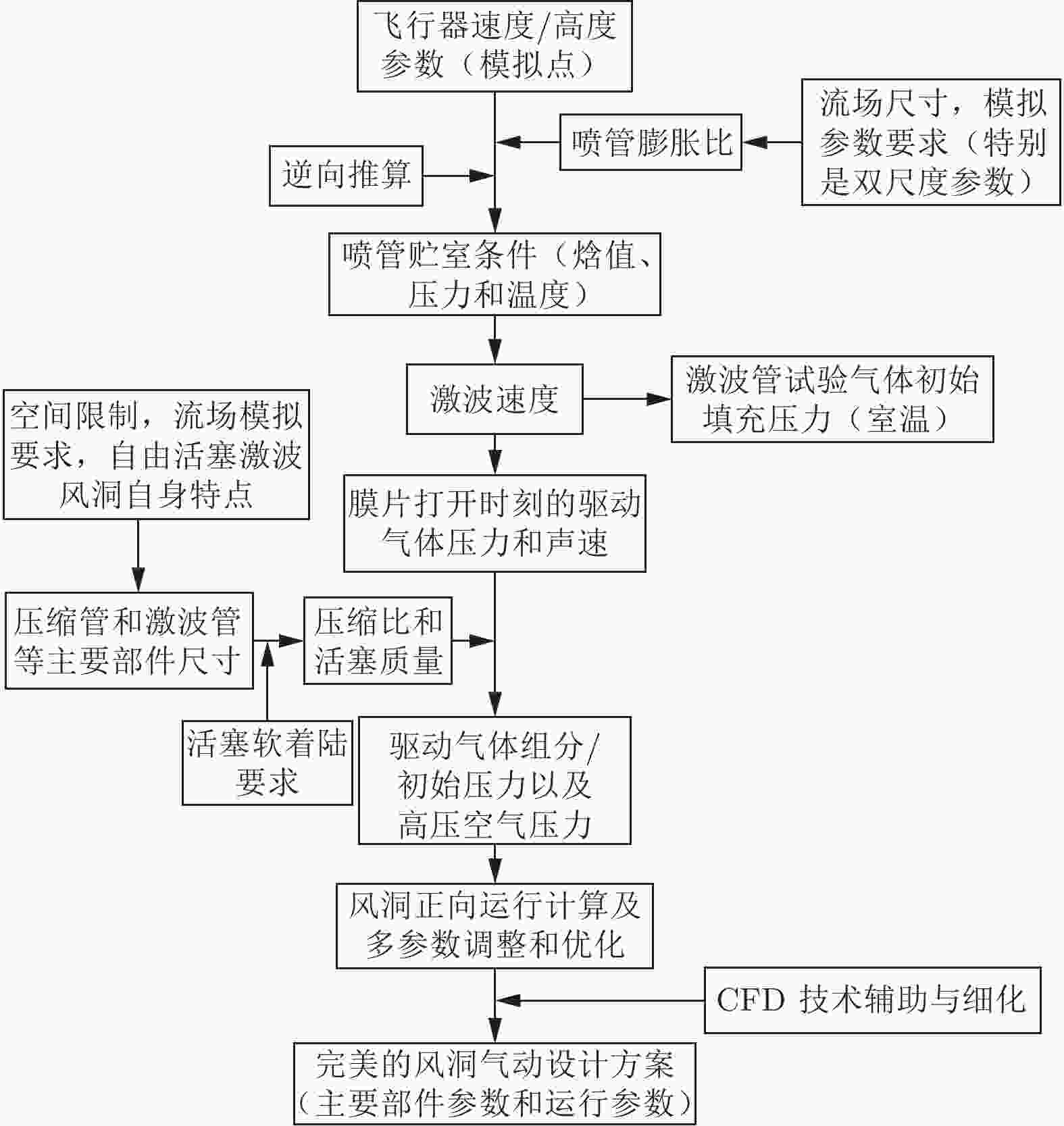
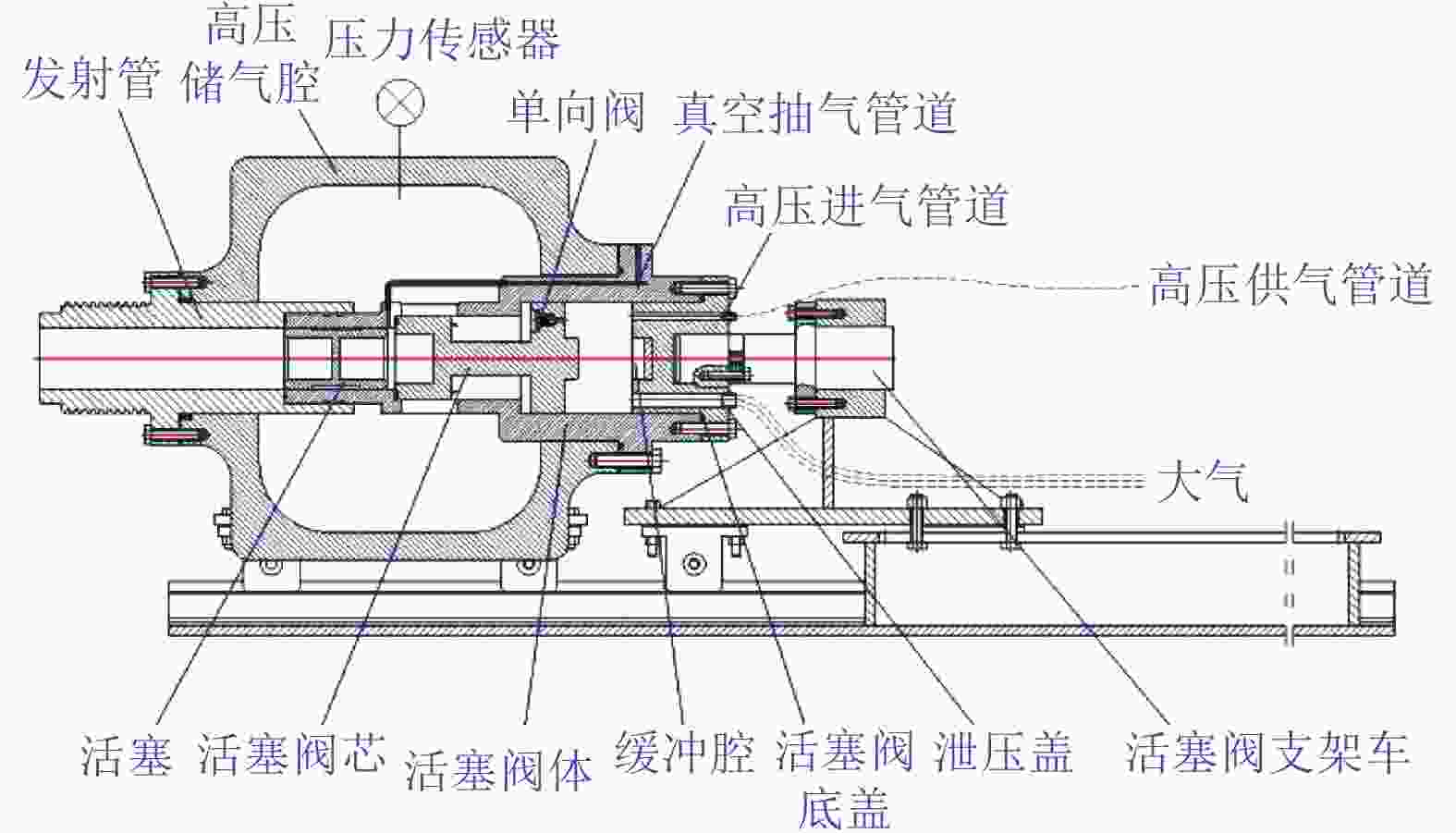
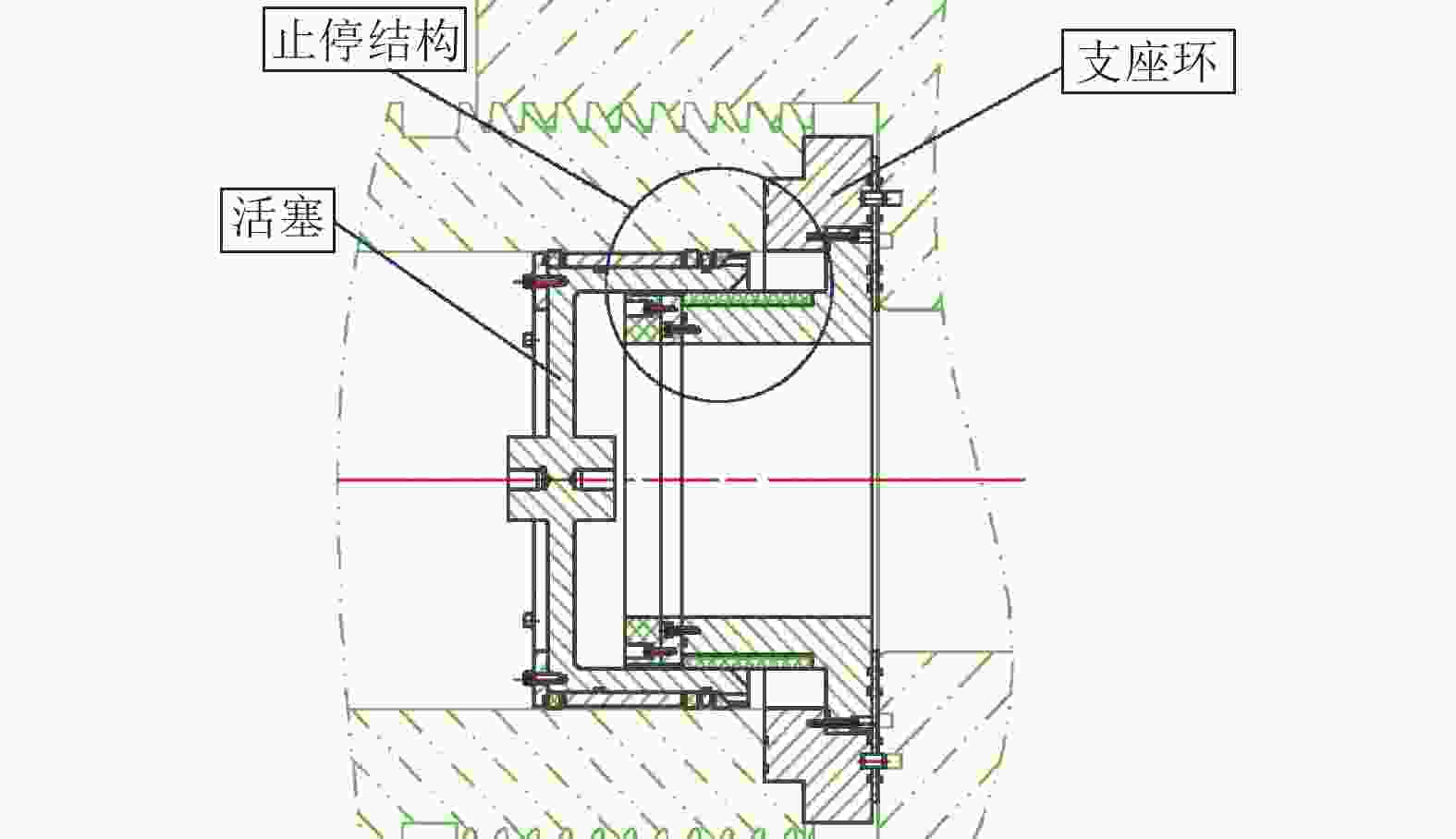
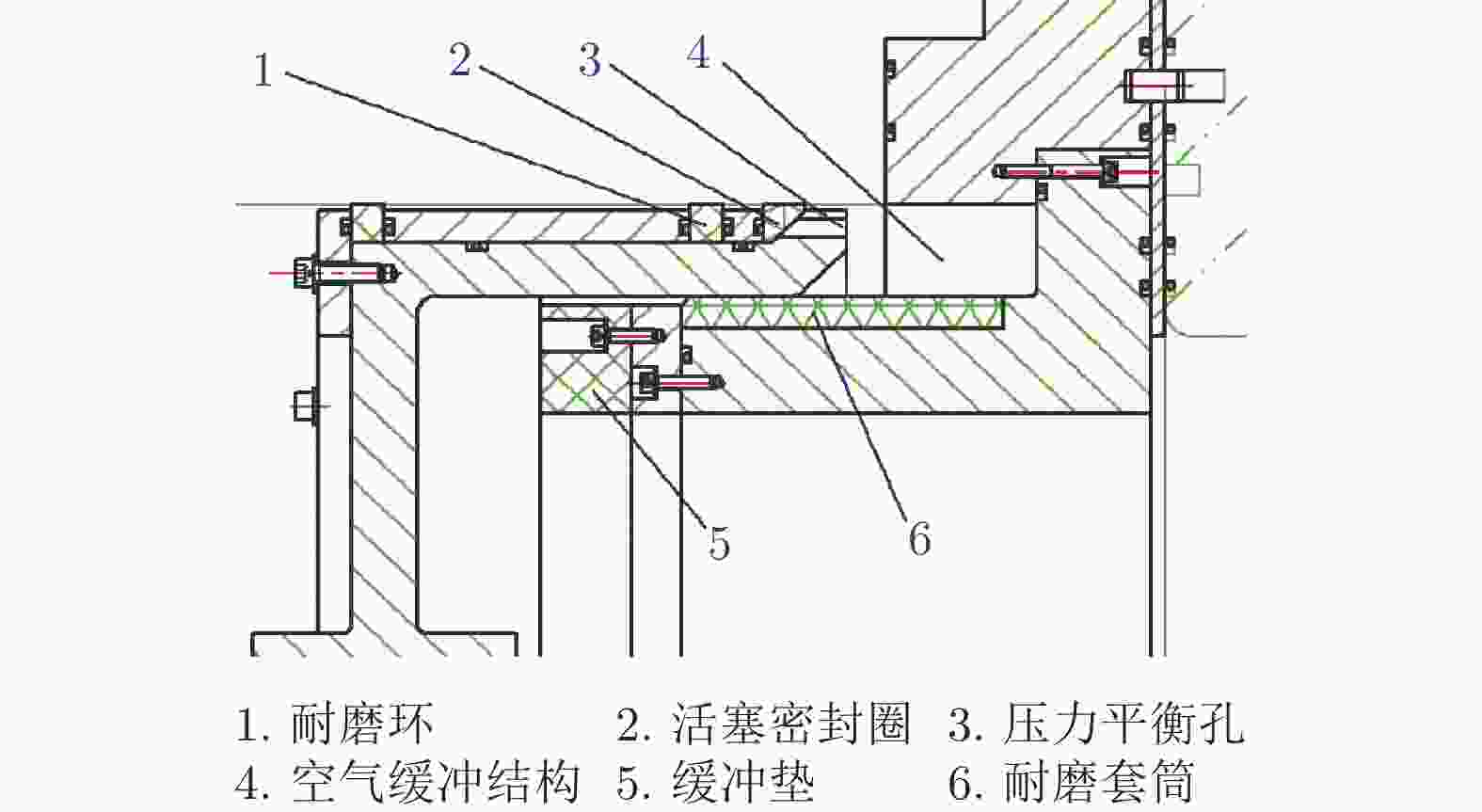
摘要: 中国航天空气动力技术研究院建设的2.0 m高能脉冲风洞(FD–21)是一座自由活塞激波风洞,该风洞拓展了中国航天空气动力技术研究院原有的试验能力。主要介绍了这座风洞的研制过程和若干关键技术。在吸收国外相关理论和经验的同时,独立解决了诸多关键性的气动问题,并通过逆向设计流程完成了风洞的气动设计。基于这些努力,高能脉冲风洞在建造过程中,逐步克服了活塞发射、活塞止停和全浮动风洞支撑等工程技术难点。FD–21的成功研制标志着自由活塞驱动技术的全面掌握,缩小了我国高焓地面模拟设备与国外的差距,对提升我国高超声速领域的研究水平具有重要意义。Abstract: The Φ2.0 m high energy pulsed tunnel (FD–21) of CAAA is a free piston shock tunnel, which expands the test capability of CAAA. This paper mainly introduces the develop-ment process and key technologies of the FD–21 tunnel. Many key aerodynamic problems are settled independently. And the aerodynamic design is completed by the reverse design method. Based on these efforts, the engineering technical difficulties such as piston launch, piston stop, full floating support have been gradually overcome during the construction of the FD–21 tunnel. The successful development of the FD–21 tunnel marks the mastery of the free piston driving techno-logy, reduces the gap between China and some foreign countries, and improves the hypersonic research level in China greatly.
-
Key words:
- shock tunnel /
- high energy /
- free piston /
- aerodynamic design /
- full floating support
-
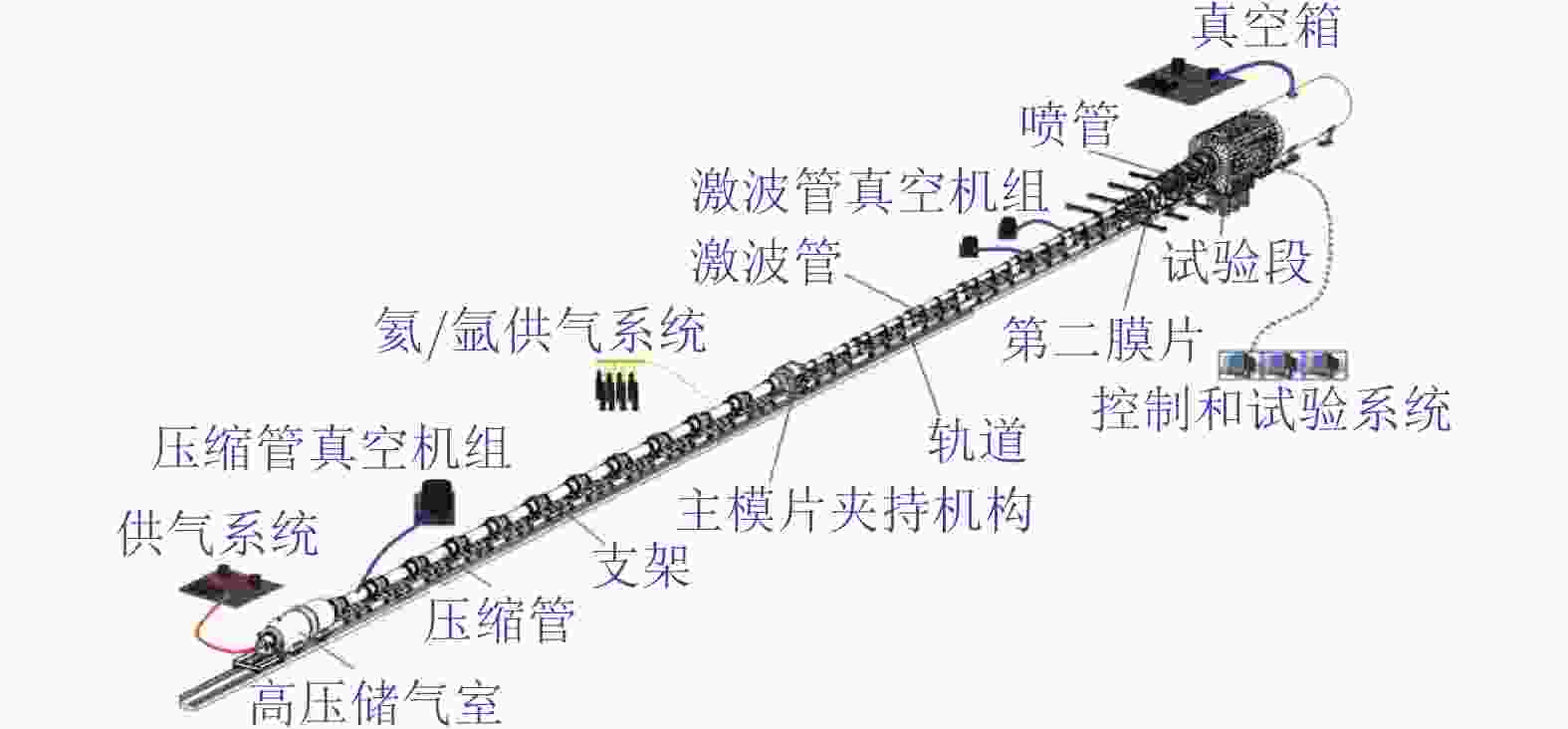
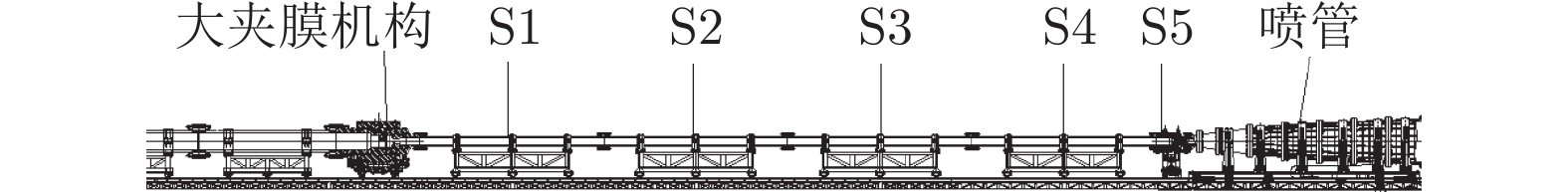
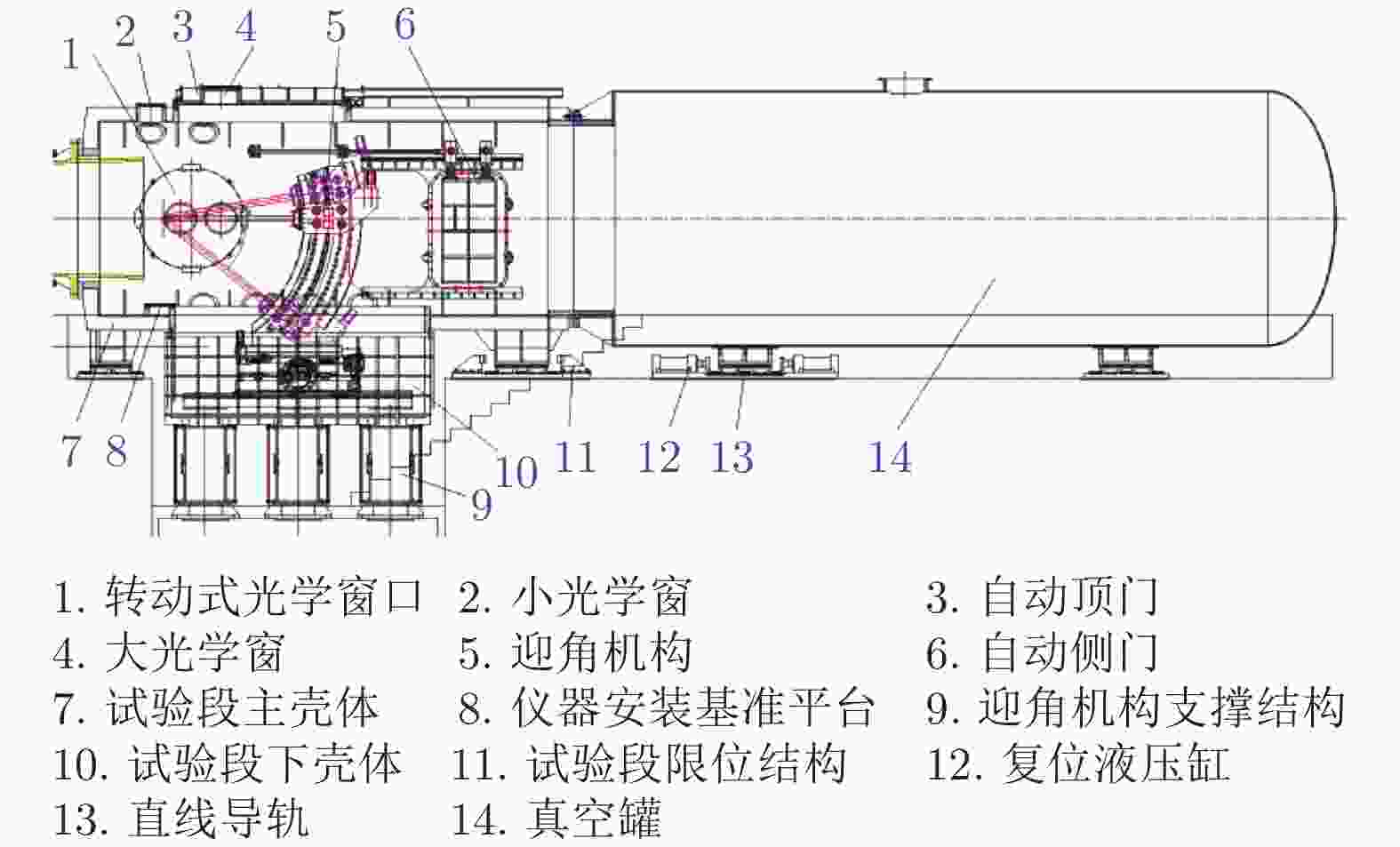
表 1 FD−21风洞主要部件参数
Table 1. Parameters of FD−21 tunnel
部件 参数 高压储气室 容积24 m3、耐压20.0 MPa 压缩管 总长72.5 m、内径668 mm、耐压70.0 MPa 激波管 总长36.0 m、内径290 mm、耐压100.0 MPa 试验段 总容积230 m3、耐压0.3 MPa、最大真空度1 Pa 型面喷管 出口直径1.2 m或2.0 m 活塞重量 205、275、400、600 kg 高压储气室 容积24 m3、耐压20.0 MPa 表 2 FD−21风洞的运行状态
Table 2. Flow conditions of FD−21 tunnel
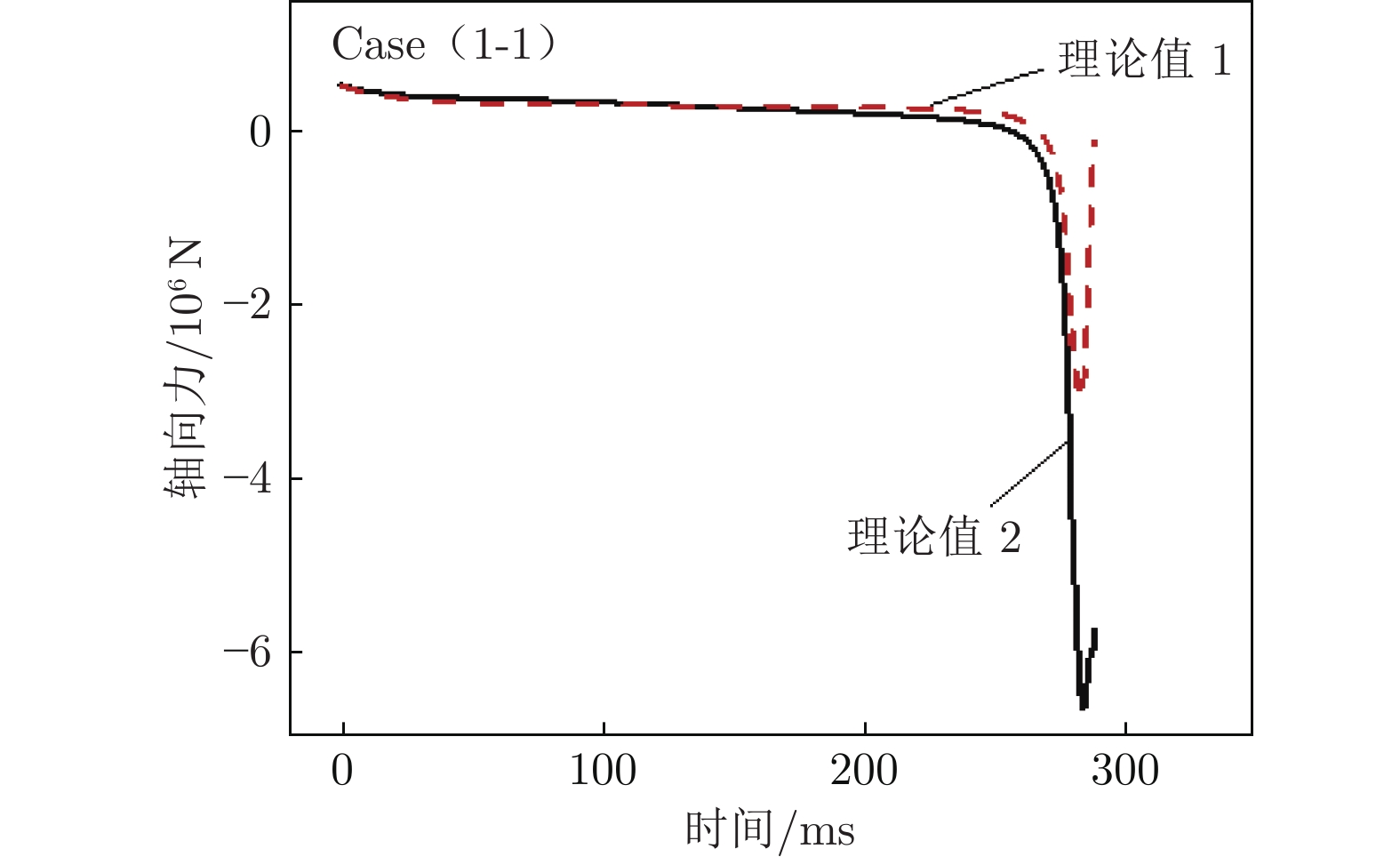
Case pr/MPa pc/kPa Mp/kg p1/kPa p0/MPa T0/K p/Pa T/K v/(m·s-1) Ma 1-1 2.85 30.0 205 61 9.2 2700 240 161 2417 9.78 1-2 2.85 30.0 205 10 5.7 4700 191 362 3375 9.10 1-3 7.50 38.5 275 80 20.3 4050 578 301 3160 9.29 -
[1] MELANSON M, CHANG M, BAKER W. Wind tunnel test-ing's future: a vision of the next generation of wind tunnel test requirements and facilities[C]//Proc of the 48th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting Including the New Horizons For-um and Aerospace Exposition. 2010. doi: 10.2514/6.2010-142 [2] CANDLER G, MAVRIPLIS D, TREVINO L. Current status and future prospects for the numerical simulation of hyper-sonic flows[C]//Proc of the 47th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting including The New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition. 2009. doi: 10.2514/6.2009-153 [3] MELANSON M. An assessment of the increase in wind tun-nel testing requirements for airvehicle development over the last 50 years[C]//Proc of the 46th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit. 2008. doi: 10.2514/6.2008-830 [4] KEGELMAN J, DANEHY P, SCHWARTZ R. Advanced capabilities for wind tunnel testing in the 21st century[C]// Proc of the 48th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting Includ-ing the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition. 2010. doi: 10.2514/6.2010-1304 [5] GU S D,OLIVIER H. Capabilities and limitations of exist-ing hypersonic facilities[J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences,2020,113:100607. doi: 10.1016/j.paerosci.2020.100607 [6] HANNEMANN K, ITOH K, MEE D J, et al. Free piston shock tunnels HEG, HIEST, T4 and T5[M]//Experimental Methods of Shock Wave Research. Cham: Springer Interna-tional Publishing, 2015: 181-264. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-23745-9_7 [7] GLASS I I, HALL J G. Shock tubes: Handbook of Super-sonic Aerodynamic Section18[R]. NAVORD Report 1488, 1959. [8] LUKASIEWICZ J. Experiment Methods of Hypersonic[M]. New York: Marcel Dekker INC, 1973. [9] GAI S L. Free piston shock tunnels: developments and capabilities[J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences,1992,29(1):1-41. doi: 10.1016/0376-0421(92)90002-Y [10] STALKER R J. Modern developments in hypersonic wind tunnels[J]. The Aeronautical Journal,2006,110(1103):21-39. doi: 10.1017/s0001924000004346 [11] 朱浩. 自由活塞激波风洞理论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019.ZHU H. The theory of free piston shock tunnels[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2019. [12] TANNO H, KOMURO T, SATO K, et al. Aeroheating measurement of Apollo shaped capsule with boundary layer trip in the free-piston shock tunnel HIEST[C]//Proc of the 52nd Aerospace Sciences Meeting. 2014. doi: 10.2514/6.2014-0434 [13] HOLDEN M S. Aerothermal and propulsion ground testing that can be conducted to increase chances for successful hy-pervelocity flight experiments[R]. RTO-EN-AVT-130, 2005. [14] 朱浩,江海南,张冰冰. 自由活塞激波风洞的入射激波衰减[J]. 航空学报,2017,38(12):121328.ZHU H,JIANG H N,ZHANG B B. Attenuation of incident shock waves in free piston shock tunnels[J]. Acta Aeronau-tica et Astronautica Sinica,2017,38(12):121328. [15] HORNUNG H G,SUDANI N,VALIFERDOWSI B. Test time increase by delaying driver gas contamination for reflec-ted shock tunnels[J]. AIAA Journal,2000,38:1497-1503. doi: 10.2514/3.14574 [16] 朱浩,江海南,张冰冰. 自由活塞驱动的双模式风洞[C]//力学大会论文集. 2019. [17] 郑永熙. FD−20风洞设备[R]. 中国航空气动力技术研究院技术报告No. 1003 FD 20-01-02,1970. [18] 李明智. FD−22重活塞炮风洞实施论证报告[R]. 中国航空气动力技术研究院技术报告No. 1003 FD22-04-02,1995. [19] 朱浩. 自由活塞激波风洞理论设计与运行模拟[R]. 中国航空气动力技术研究院博士后研究工作报告, 2012. [20] 朱浩,沈清,宫建. 自由活塞激波风洞定压驱动时间研究[J]. 空气动力学学报,2014,32(1):45-50,56. doi: 10.7638/kqdlxxb-2012.0048ZHU H,SHEN Q,GONG J. The constant pressure time of piston driver in free piston shock tunnel[J]. Acta Aerody-namica Sinica,2014,32(1):45-50,56. doi: 10.7638/kqdlxxb-2012.0048 [21] 朱浩, 江海南, 张冰冰. 高能脉冲风洞总体设计方案[R]. 中国航空气动力技术研究院技术报告No. 0204-16-01, 2016. [22] 张冰冰, 朱浩, 李辰. 活塞压缩器验证性平台试验报告[R]. 中国航空气动力技术研究院技术报告No. 0204-15-05, 2015. [23] 谌君谋, 张冰冰. FD−21高能脉冲风洞试验实施大纲(模拟点3活塞调试)[R]. 中国航空气动力技术研究院技术报告No. 0204-17-12, 2017. [24] 易翔宇, 陈星, 毕志献, 等. 自由活塞激波风洞压缩管: 激波管流动分析及4000 K状态调试[C]//首届中国空气动力学大会论文集. 2018. [25] 谌君谋, 陈星, 毕志献, 等. FD−21高焓激波风洞最新进展[C]//第19届全国激波与激波管学术会议论文集. 2020. [26] 卢洪波,陈星,谌君谋,等. 新建高焓激波风洞Ma=8飞行模拟条件的实现与超燃实验[J]. 气体物理,2019,4(5):13-24. doi: 10.19527/j.cnki.2096-1642.0782LU H B,CHEN X,SHEN J M,et al. Flight condition achievement of Mach number 8 in a new shock tunnel of CAAA and its scramjet experimental investigation[J]. Physics of Gases,2019,4(5):13-24. doi: 10.19527/j.cnki.2096-1642.0782 [27] 张冰冰,谌君谋. 高能脉冲风洞状态三调试第二阶段试验报告: 活塞极限运行及止停机构性能试验报告[R]. 中国航空气动力技术研究院技术报告No. 0204-17-15,2017. [28] 朱浩, 宫建. 自由活塞激波风洞理论设计撮要[C]//第16届全国激波与激波管学术会议论文集. 2015. [29] HORNUNG H G. The piston motion in a free piston driver for shock tubes and tunnels[R]. GALCIT Report FM 88-1, 1988. [30] 朱浩,张冰冰,余亦甫. 膜片非理想打开行为对自由活塞激波风洞运行的影响[J]. 实验流体力学,2020,34(1):55-59. doi: 10.11729/syltlx20190023ZHU H,ZHANG B B,YU Y F. Effect of non-ideal opening behavior of diaphragm on the operation of free piston shock tunnels[J]. Journal of Experiments in Fluid Mechanics,2020,34(1):55-59. doi: 10.11729/syltlx20190023 [31] ALPHER R A,WHITE D R. Flow in shock tubes with area change at the diaphragm section[J]. Journal of Fluid Mecha-nics,1958,3(5):457-470. doi: 10.1017/s0022112058000124 [32] 陈强. 激波管流动的理论和试验技术[M]. 中国科学技术大学出版社, 1979. [33] ZHU H,JIANG H N. Influence of shock attenuation on tailored operation in free piston shock tunnel[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics,2021,34(2):279-287. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2020.08.025 [34] EGGERS A J. One dimensional flows of an imperfect diatomic gas[R]. NACA TN-1681, 1949. [35] MARINEAU E, HORNUNG H. High-enthalpy nonequilib-rium nozzle flow of air: experiments and computations[C]// Proc of the 39th AIAA Fluid Dynamics Conference. 2009. doi: 10.2514/6.2009-4216 [36] TAKAHASHI M, KODERA M, ITOH K, et al. Influence of thermal non-equilibrium on nozzle flow condition of high enthalpy shock tunnel HIEST[C]//Proc of the 16th AIAA/ DLR/DGLR International Space Planes and Hypersonic Systems and Technologies Conference. 2009. doi: 10.2514/6.2009-7267 [37] MATSUZAKI R. Design of contoured nozzle for arc-heated wind tunnels[C]//Proc of the 25th Plasmadynamics and Lasers Conference. 1994. doi: 10.2514/6.1994-2593 [38] LASTER M, JORDAN J, MERKLE C, et al. Remarks on the design of hypersonic high Reynolds number nozzles with energy addition[C]//Proc of the 25th AIAA Aerodynamic Measurement Technology and Ground Testing Conference. 2006. doi: 10.2514/6.2006-2957 -







 下载:
下载: