Experimental study on drag reduction of L-shaped bluff body by AC-DBD plasma actuation
-
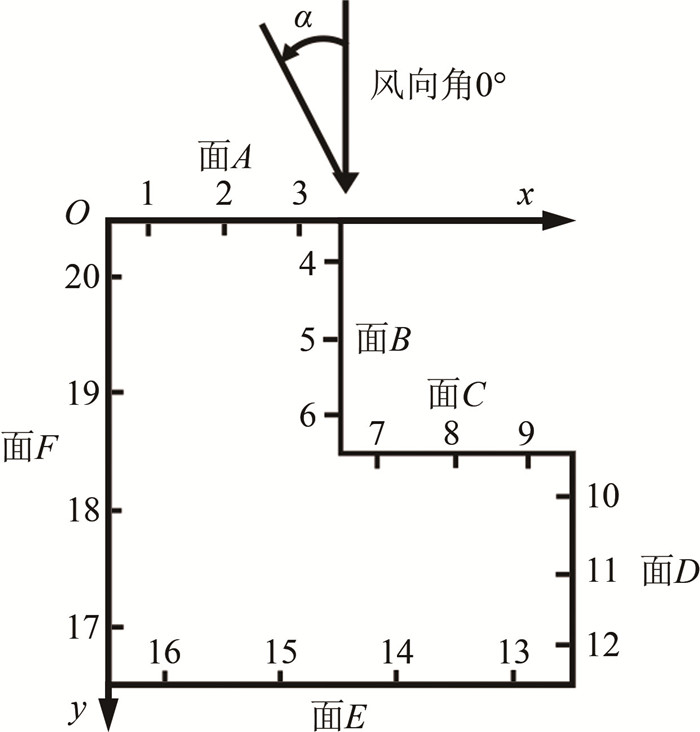
摘要: 等离子体流动控制是一种应用广泛的主动流动控制技术。为进一步研究其机理、拓展其应用范围,针对L形截面钝体模型,采用3种AC-DBD(介质阻挡放电)等离子体激励器布置形式,比较了施加激励后的减阻效果,并对减阻机理进行了研究。实验在南京航空航天大学0.8 m低速直流风洞中进行(风向角0°、来流速度2~8 m/s),激励器布置形式为顺来流前缘激励、逆来流前缘激励和拐角激励。研究结果表明:不同来流速度下,等离子体激励器对L形截面钝体都有一定的减阻效果,且减阻效果随流速增大而降低;拐角激励减阻效果最佳,逆来流前缘激励次之,顺来流前缘激励最差;通过流场分析,说明了激励器布置形式变化产生了不同的扰动效果;不同的流动控制机理是影响减阻效果的关键因素。Abstract: Plasma flow control is a widely used active flow control method. In order to further expand the application scope and understand the actuation mechanism, three kinds of AC-DBD (Dielectric Barrier Discharge) plasma actuator layout forms are used to compare the drag reduction capabilities of the L-shaped model after actuation, and the drag reduction mechanism is studied. The experiment is carried out in a low-speed DC wind tunnel, with a wind direction angle of 0°, and a wind speed of 2-8 m/s. These different actuators layout forms are the plasma actuator placed close to the leading edge along the incoming flow direction, the plasma actuator placed close to the leading edge against the incoming flow direction, and the plasma actuator arranged at the corner, respectively. Research shows that plasma actuators under different wind speed conditions have a certain control effect on drag reduction of bluff bodies, and the control ability decreases with the increase of wind speed. The plasma actuator placed in the corner produces the best control effect, and the drag reduction rate can reach more than 13% at low speed. The plasma actuator placed close to the leading edge against the incoming flow direction produces a similar effect. The drag reduction rate of the plasma actuator near the leading edge along the inflow direction can only reach about 7% at most. By analyzing the flow field, it is shown that the change of layout position produces different disturbance effects. Different flow control mechan-isms are the key factors affecting the actuation effect.
-
表 1 实验工况表
Table 1. Experimental conditions
激励器布置形式 风向角/(°) 来流速度/(m·s-1) 顺来流前缘激励 0 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 逆来流前缘激励 0 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 拐角激励 0 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 -
[1] 吴瑾, 夏逸鸣, 张丽芳. 土木工程结构抗风设计[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2007. [2] SIMIU E, YEO D H. Wind effects on structures: modern structural design for wind[M/OL]. 4th ed. New Jersey: Wiley-Blackwell, 2019: 55-71. [2020-08-19]. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/book/10.1002/9781119375890.doi: 10.1002/9781119375890 [3] KENNEDY J, NERI E, BENNETT G J. The reduction of main landing gear noise[C]//Proc of the 22nd AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference. 2016 doi: 10.2514/6.2016-2900 [4] DIPANKAR A, SENGUPTA T K, TALLA S B. Suppression of vortex shedding behind a circular cylinder by another control cylinder at low Reynolds numbers[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2007, 573: 171-190. doi: 10.1017/s002211200600382x [5] BAO Y, TAO J. The passive control of wake flow behind a circular cylinder by parallel dualplates[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2013, 37: 201-219. doi: 10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2012.11.002 [6] MARUTA E, KANDA M, SATO J. Effects on surface roughness for wind pressure on glass and cladding ofbuildings[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 1998, 74-76: 651-663. doi: 10.1016/S0167-6105(98)00059-2 [7] TANAKA H, TAMURA Y, OHTAKE K, et al. Experimental investigation of aerodynamic forces and wind pressures acting on tall buildings with various unconventional configurations[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2012, 107-108: 179-191. doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2012.04.014 [8] 张耀春, 秦云, 王春刚. 洞口设置对高层建筑静力风荷载的影响研究[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2004, 25(4): 112-117, 123. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6869.2004.04.018ZHANG Y C, QIN Y, WANG C G. Research on the influence of openings to static wind load of highrise buildings[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2004, 25(4): 112-117, 123. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6869.2004.04.018 [9] 顾明, 王凤元, 全涌, 等. 超高层建筑风荷载的试验研究[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2000, 21(4): 48-54. doi: 10.14006/j.jzjgxb.2000.04.007GU M, WANG F Y, QUAN Y, et al. Experimental study on dynamic wind loads on super-tall buildings[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2000, 21(4): 48-54. doi: 10.14006/j.jzjgxb.2000.04.007 [10] 张正维, 全涌, 顾明, 等. 凹角对方形截面高层建筑基底气动力系数的影响研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 2013, 46(7): 58-65. doi: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2013.07.017ZHANG Z W, QUAN Y, GU M, et al. Effects of corner recession modification on aerodynamic coefficients of square high-rise buildings[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2013, 46(7): 58-65. doi: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2013.07.017 [11] BANDI E K, KIM Y, YOSHIDA A, et al. Aerodynamic characteristics of triangular-section tall buildings with different helical angles[C]//Proc of the ICWE13-International Conference on Wind Engineering'13. 2011. [12] 战培国, 程娅红, 赵昕. 主动流动控制技术研究[J]. 航空科学技术, 2010, 21(5): 2-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5453.2010.05.001ZHAN P G, CHENG Y H, ZHAO X. A review of active flow controltechnology[J]. Aeronautical Science and Technology, 2010, 21(5): 2-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5453.2010.05.001 [13] FENG L H, WANG J J, PAN C. Effect of novel synthetic jet on wake vortex shedding modes of a circular cylinder[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2010, 26(6): 900-917. doi: 10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2010.05.003 [14] 王佳, 邓飞, 张衡. 壁面振动对流场特性影响的数值模拟预报[J]. 声学技术, 2013, 32(4, Pt. 2): 76-79. https://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-SXJS201308001022.htmWANG J, DENG F, ZHANG H. The numerical simulation forecast of the characteristic on wall oscillation to the flow field[J]Technical Acoustics, 2013, 32(4, Pt. 2): 76-79. https://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-SXJS201308001022.htm [15] 董宇飞, 魏中磊. 流线型轴对称钝体尾迹特性及其声激励控制[J]. 力学学报, 1999, 31(6): 682-693. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LXXB199906006.htmDONG Y F, WEI Z L. Experimental investigation of the wake of axisymmetric bluff body and its control by means of acoustic forcing[J]. Acta Mechanica Sinica, 1999, 31(6): 682-693. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LXXB199906006.htm [16] 张立启. 三维圆柱绕流与涡激振动的行波壁控制方法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2019.ZHANG L Q. Study on traveling wave wall control method of flow around the three-dimensional cylinder and vortex induced vibration[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2019. doi: 10.27061/d.cnki.ghgdu.2019.002261 [17] 郑朝荣, 张耀春. 高层建筑风荷载减阻的吸气方法数值研究[J]. 应用基础与工程科学学报, 2010, 18(1): 80-90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0930.2010.01.010ZHENG C R, ZHANG Y C. Numerical investigation of the wind-load reduction for a high-rise building by suction[J]. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering, 2010, 18(1): 80-90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0930.2010.01.010 [18] 张洪福. 超高层建筑横风向风致效应定常吸气控制[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2013.ZHANG H F. Steady suction for controlling Across-wind-induced effects of super High-risebuildings[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2013. [19] SHTENDEL T, SEIFERT A. Three-dimensional aspects of cylinder drag reduction by suction and oscillatoryblowing[J]. International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow, 2014, 45: 109-127. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatfluidflow.2013.10.009 [20] 史志伟, 杜海, 李铮, 等. 等离子体流动控制技术原理及典型应用[J]. 高压电器, 2017, 53(4): 72-78. doi: 10.13296/j.1001-1609.hva.2017.04.013SHI Z W, DU H, LI Z, et al. Mechanism and applications of plasma flow control technology[J]. High Voltage Apparatus, 2017, 53(4): 72-78. doi: 10.13296/j.1001-1609.hva.2017.04.013 [21] WANG J J, CHOI K S, FENG L H, et al. Recent developments in DBD plasma flow control[J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 2013, 62: 52-78. doi: 10.1016/j.paerosci.2013.05.003 [22] 龙玥霄, 李华星, 孟宣市. AC和NS等离子体激励对细长前体分离涡流场的控制[J]. 航空工程进展, 2014, 5(3): 358-363. doi: 10.16615/j.cnki.1674-8190.2014.03.014LONG Y X, LI H X, MENG X S. Flow control over a slender forebody using AC and NS-DBD plasmaactuators[J]. Advances in Aeronautical Science and Engineering, 2014, 5(3): 358-363. doi: 10.16615/j.cnki.1674-8190.2014.03.014 [23] 孟宣市, 杨泽人, 陈琦, 等. 低雷诺数下层流分离的等离子体控制[J]. 航空学报, 2016, 37(7): 2112-2122. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2015.0244MENG X S, YANG Z R, CHEN Q, et al. Laminar separation control at low Reynolds numbers using plasmaactuation[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2016, 37(7): 2112-2122. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2015.0244 [24] 聂万胜, 程钰锋, 车学科. 介质阻挡放电等离子体流动控制研究进展[J]. 力学进展, 2012, 42(6): 722-734. doi: 10.6052/1000-0992-11-161NIE W S, CHENG Y F, CHE X K. A review on dielectric barrier discharge plasma flowcontrol[J]. Advances in Mechanics, 2012, 42(6): 722-734. doi: 10.6052/1000-0992-11-161 [25] 吴云, 李应红. 等离子体流动控制研究进展与展望[J]. 航空学报, 2015, 36(2): 381-405. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2014.0246WU Y, LI Y H. Progress and outlook of plasma flow control[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2015, 36(2): 381-405. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2014.0246 [26] 马力群, 冯立好. 放置于驻点的合成射流控制圆柱涡脱落模式的实验研究[J]. 中国科学(技术科学), 2013, 43(2): 208-219. doi: 10.1007/s11431-012-5074-4MA L Q, FENG L H. Experimental investigation on control of vortex shedding mode of a circular cylinder using synthetic jets placed at stagnationpoints[J]. Scientia Sinica Technologica, 2013, 43(2): 208-219. doi: 10.1007/s11431-012-5074-4 [27] 孙卫威. 等离子体流动控制技术在低矮建筑物应用的研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2017.SUN W W. The application research of plasma flow control technology on low rise buildings[D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2017. [28] 郑朝荣, 张耀春. 吸气方法在高层建筑风荷载减阻中的应用[J]. 工程力学, 2009, 26(z1): 51-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCLX2009S1016.htmZHENG C R, ZHANG Y C. Application of the suction method to reduce the wind load on high-rise building[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2009, 26(z1): 51-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCLX2009S1016.htm -








 下载:
下载: