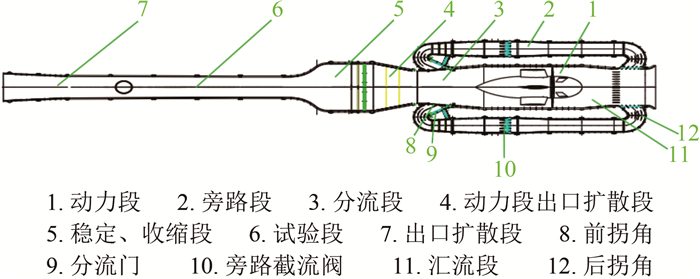
Active turbulence simulation study of wind loads on standard low-rise building
-
摘要: 采用主动与被动湍流相结合的方法,在阵风风洞中模拟了不同湍流强度和湍流积分尺度的流场,开展了1:50低矮建筑标准模型测压试验研究。针对气流分离再附流动作用下的屋面中轴线区域和锥形涡作用下的屋面角部边缘区域,着重分析了不同来流湍流强度和顺风向湍流积分尺度影响下的风压变化规律。研究结果表明:湍流强度对气流分离作用下的迎风屋面屋檐区域以及锥形涡作用下的屋面角部边缘区域的平均风压系数、脉动风压系数和峰值负压系数均有显著影响;而湍流积分尺度对这些区域的平均风压系数影响甚微,脉动风压系数和峰值负压系数(绝对值)随湍流积分尺度的增大而有所增大。Abstract: This paper presents model scale tests for 1:50 geometrical scale laboratory modeling for the Texas Tech University (TTU) test building in a gust wind tunnel. This tunnel is able to add low frequency turbulence components for generation of large-scale turbulent flows by the conventional passive simulation technique or a technique combining active and passive turbulence generation devices. This paper mainly studies the effects of the turbulence integral length scale and turbulence intensity on wind-induced pressures on the flat roof of TTU full scale building. The results imply that the turbulence intensity has significant influence on the mean wind pressure coefficients at the leading edge of the flat roof under the separation bubble and in the corner zone for the conical vortex flow regime. Meanwhile, the turbulence intensity plays a predominant role in producing the fluctuation and peak pressure at the leading edge or in the corner area. On the other hand, the turbulence integral length scale has no noticeable influence on the mean wind pressure coefficients at the leading edge or in the corner zone. However, the turbulence integral scale length plays a slightly significant role in producing the fluctuation and peak pressure at the leading edge or in the corner zone.
-
表 1 主动阵风风洞风场参数试验值和现场实测值
Table 1. Experimental values and field measured values of active gust wind tunnel wind field parameters
高度 流场工况 Iu/% Iv/% Iw/% Lu/m Lv/m Lw/m 10 m Full scale 19.7 14.5 8.8 125.0 58.5 31.5 CBL-1 15.8 12.9 9.5 31.0 14.0 8.0 CBL-1 and Active Gust 17.4 12.0 8.7 81.5 16.0 8.5 CBL-2 12.6 9.4 7.1 24.5 7.0 4.5 3.950 m Full scale 21.7 16.0 5.5 93.8 59.0 14.7 CBL-1 17.3 14.7 9.5 27.5 15.5 4.0 CBL-1 and Active Gust 18.3 14.1 9.3 52.0 16.0 4.0 CBL-2 14.8 10.7 8.3 23.0 5.5 3.5 注:湍流积分尺度(风洞试验值)系依据泰勒的对流“凝固湍流”假设、对各向脉动分量进行自相关函数积分计算得到,对应的实测值根据几何模型比例(1:50)进行了相应转换。 -
[1] CERMAK J E. Progress in physical modeling for wind engineering[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 1995, 54/55:439-455. doi: 10.1016/0167-6105(94)00064-K [2] 裴城, 马存明, 王明志, 等.紊流积分尺度对典型桥梁断面静力系数影响规律的风洞试验研究[J].土木工程学报, 2020, 53(1):64-72. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=tmgcxb202001008PEI C, MA C M, WANG M Z, et al. Wind tunnel tests on the influence of turbulent integral scale on aerostatic coefficients of typical bridge section[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2020, 53(1):64-72. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=tmgcxb202001008 [3] 陈凯, 毕卫涛, 魏庆鼎.振动尖塔对风洞模拟大气湍流边界层的作用[J].空气动力学学报, 2003, 21(2):211-217. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kqdlxxb200302012CHEN K, BI W T, WEI Q D. Vibrational spires method in wind tunnel simulation of atmospheric boundary layer[J]. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 2003, 21(2):211-217. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kqdlxxb200302012 [4] NISHI A, KIKUGAWA H, MATSUDA Y, et al. Turbulence control in multiple-fan wind tunnels[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 1997, 67/68:861-872. doi: 10.1016/S0167-6105(97)00124-4 [5] CAO S Y, NISHI A, KIKUGAWA H, et al. Reproduction of wind velocity history in a multiple fan wind tunnel[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2002, 90(12-15):1719-1729. doi: 10.1016/S0167-6105(02)00282-9 [6] 潘韬, 赵林, 曹曙阳, 等.主动来流条件类平板断面气动力荷载效应分析[J].实验流体力学, 2010, 24(6):32-37, 56. http://www.syltlx.com/CN/abstract/abstract9904.shtmlPAN T, ZHAO L, CAO S Y, et al. Analysis of aerodynamic load effects on thin plat section under active control flow condition[J]. Journal of Experiments in Fluid Mechanics, 2010, 24(6):32-37, 56. http://www.syltlx.com/CN/abstract/abstract9904.shtml [7] 陈彬, 姚裕, 易弢, 等.基于回流多风扇主动控制引导风洞的风场模拟试验[J].南京航空航天大学学报, 2019, 51(3):374-381. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=njhkht201903015CHEN B, YAO Y, YI T, et al. Wind field simulation in small-scale model of closed-circuit multiple controlled fan wind tunnel[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics, 2019, 51(3):374-381. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=njhkht201903015 [8] HAAN F L Jr, SARKAR P P, SPENCER-BERGER N J. Development of an active gust generation mechanism on a wind tunnel for wind engineering and industrial aerodynamics applications[J]. Wind and Structures, 2006, 9(5):369-386. doi: 10.12989/was.2006.9.5.369 [9] HUANG P, CHOWDHURY A G, BITSUAMLAK G, et al. Development of devices and methods for simulation of hurricanewinds in a full-scale testing facility[J]. Wind and Structures, 2009, 12(2):151-177. [10] ASGHARI MOONEGHI M, IRWIN P, CHOWDHURY A G. Partial turbulence simulation method for predicting peak wind loads on small structures and building appurtenances[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2016, 157:47-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2016.08.003 [11] BROWN T M, LIU Z Z, MORRISON M J. Comparison of field and full-scale laboratory pressure data at the IBHS research center[C]//Proceedings of the 13rd International Conference on Wind Engineering. 2011. [12] HANGAN H, REFAN M, JUBAYER C, et al. Novel techniques in wind engineering[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2017, 171:12-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2017.09.010 [13] 黄汉杰, 王卫华, 蒋科林.大比例TTU模型表面风压分布试验研究[J].建筑结构学报, 2016, 37(12):58-64, 73. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jzjgxb201612008HUANG H J, WANG W H, JIANG K L. Experimental research on surface wind pressure distribution on large scale TTU model[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2016, 37(12):58-64, 73. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jzjgxb201612008 [14] LEVITAN M L, MEHTA K C. Texas tech field experiments for wind loads part 1:building and pressure measuring system[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 1992, 43(1-3):1565-1576. doi: 10.1016/0167-6105(92)90372-H [15] LEVITAN M L, MEHTA K C. Texas tech field experiments for wind loads part II:meteorological instrumentation and terrain parameters[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 1992, 43(1-3):1577-1588. doi: 10.1016/0167-6105(92)90373-I [16] HAM H J, BIENKIEWICZ B. Wind tunnel simulation of TTU flow and building roof pressure[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 1998, 77/78:119-133. doi: 10.1016/S0167-6105(98)00137-8 [17] SMITH D A, MORSE S M, MEHTA K C. WERFL data description user's manual: Wind Engineering Research Field Laboratory selected data sets for comparison to model-scale, full-scale and computational fluid dynamics simulations[EB/OL]. (2017)[2019-10-21]. http://www.depts.ttu.edu/nwi/Pubs/ReportsJournals/ReportsJournals/WERFL_Data_Description_2_08_17b.pdf. -








 下载:
下载: