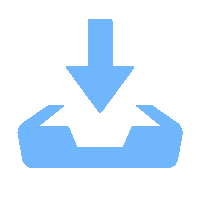
Measurement of CO concentration in flat flame based on mid-infrared absorption spectroscopy
-
摘要: CO是碳氢化合物燃烧的主要产物之一,准确测量超燃冲压发动机出口的CO浓度是评估碳氢燃料燃烧效率的重要依据。中红外波段的CO谱线相较近红外而言,具有吸收更强、谱线丰富且谱线对相对孤立、不受其他气体干扰等明显优势。本文基于中红外吸收光谱技术,计算研究了CO中红外光谱特性,选择了适用于高温流场CO测量的特征谱线,设计并搭建了高温流场CO浓度检测系统,开展了气体池浓度标定和不同当量比下平面火焰CO测量验证,实现了某超燃冲压发动机出口高温流场CO测量,反映了航空煤油燃烧过程中CO浓度和温度的变化情况,为超燃冲压发动机的燃烧和流动机理研究提供了有力的研究手段和丰富的实验数据。Abstract: CO is one of the main products of hydrocarbon combustion. Accurate measurement of CO concentration at the scramjet outlet is an important basis for evaluating the combustion efficiency of the hydrocarbon fuel. Compared with the near infrared band, the CO absorption spectrum in the mid infrared band has the advantages of stronger absorption, rich spectral lines, relatively isolated spectral lines and no interference from other gases. Based on the mid infrared absorption spectrum technology, this paper studies the mid infrared spectrum characteristics of CO, selects the characteristic spectrum which is suitable for the measurement of CO in the high temperature flow field, designs and builds the CO concentration detection system in the high temperature flow field, carries out the CO measurement verification under different equivalence ratios of the plane flame, realizes the CO measurement of the high temperature flow field at the exit of a scramjet, and reflects the changes of concentration and temperature of CO during the combustion of aviation kerosene, thus providing powerful research means and abundant experimental data for the study of combustion and flow mechanism of the scramjet.
-
Key words:
- mid-infrared absorption spectroscopy /
- TDLAS /
- CO /
- flat flame /
- scramjet
-
表 1 候选谱线参数
Table 1. The parameters of candidate lines
Spectral
pairCenter
frequency
/cm-1Line strength
/(10-20 cm-1·
(mol·cm-2)-1)Low state-
energy
/cm-1Temperature
/Kpair3 2059.9147
2060.332213.40
2.75806.38280
2543.056701300 pair4 2064.3969
2064.583913.90
2.71729.67740
2489.783101300 pair3 2059.9147
2060.332210.10
3.51806.38280
2543.056701800 pair4 2064.3969
2064.583910.20
3.41729.67740
2489.783101800 表 2 不同工况下CO温度测量结果
Table 2. CO temperature measurement results under different working conditions
Order Air
/(L·min-1)CH4
/(L·min-1)ϕ Tm
/KTc
/KRelative
error1 18.9 2.39 1.2 1290.2 1237 4.3% 2 18.8 2.55 1.3 1276.7 1252 1.9% 3 18.5 2.72 1.4 1272.3 1248 1.9% -
[1] 许琳, 王高, 吕国义, 等. 超声测温技术在模拟航空发动机燃烧室温度测量中的应用[J]. 测试技术学报, 2019, 33(2): 178-184. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7449.2019.02.016XU L, WANG G, LYU G Y, et al. Ultrasonic temperature measurement technology for simulated aero-engine combustion Chambers[J]. Journal of Test and Measurement Technology, 2019, 33(2): 178-184. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7449.2019.02.016 [2] 周蕊燕, 贾译钧. 浅析航空燃烧室及其发展趋势[J]. 山东工业技术, 2016(5): 214. doi:10.16640/j.cnki.37-1222/t.2016.05. 201 [3] 胡志云, 叶景峰, 张振荣, 等. 航空发动机地面试验激光燃烧诊断技术研究进展[J]. 实验流体力学, 2018, 32(1): 33-42. doi: 10.11729/syltlx20170135HU Z Y, YE J F, ZHANG Z R, et al. Development of laser combustion diagnostic techniques for ground aero-engine testing[J]. Journal of Experiments in Fluid Mechanics, 2018, 32(1): 33-42. doi: 10.11729/syltlx20170135 [4] SPEARRIN R M, JEFFRIES J B, HANSON R K. Mid-infrared absorption sensor for measurements of CO and CO2 in propulsion flows[R]. AIAA 2014-0390, 2014. doi: 10.2514/6.2014-0390 [5] WAKEFIELD S, TOM B A, SELL B C, et al. Development of a mid-IR laser diagnostic for combustion efficiency[R]. AIAA 2014-1356, 2014. doi: 10.2514/6.2014-1356 [6] BUSA K M, BROWN M S, GRUBER M, et al. Common-path measurement of H2O, CO, and CO2 via TDLAS for combustion progress in a hydrocarbon-fueled scramjet[R]. AIAA 2016-0659, 2016. doi: 10.2514/6.2016-0659 [7] 张伯昆. 基于TDLAS的环境CO红外激光光谱监测方法研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2012.ZHANG B K. Study on infrared laser spectrum monitoring method of environmental CO based on TDLAS[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of technology, 2012. [8] 邢昆明. 基于TDLAS技术检测卷烟主流烟气中CO和CO2及抽吸耗氧量[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2017.XING K M. Detection of CO and CO2 in mainstream cigarette smoke based on TDLAS technology and oxygen consumption by suction[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2017. [9] 张保龙. 基于TDLAS的CO浓度检测系统的研究[D]. 西安: 西安科技大学, 2019.ZHANG B L. Research on CO concentration monitoring system based on TDLAS[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Science and Technology, 2019. [10] SHAO L G, FANG B, ZHENG F, et al. Simultaneous detection of atmospheric CO and CH4 based on TDLAS using a single 2.3μm DFB laser[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2019, 222: 117118. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2019.05.023 [11] 许婷. 利用可调谐半导体激光吸收光谱测量高温火焰中的CO浓度[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2011.XU T. Measurement of CO concentration in high temperature flame by tunable semiconductor laser absorption spectroscopy[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2011. [12] 彭于权. 中红外激光光谱燃烧场CO和NO污染物浓度测量[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2018.PENG Y Q. Measurement of CO and NO concentration in combustion field of mid infrared laser spectrum[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2018. [13] 陈允魁. 红外吸收光谱法及其应用[M]. 上海: 上海交通大学出版社, 1993. [14] 吴静静. 基于可调谐激光吸收光谱技术的温度测量方法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨理工大学, 2018.WU J J. Research on temperature measurement method base on tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy technology[D]. Harbin: Harbin University of Science and Technology, 2018. [15] GORDON I E, ROTHMAN L S, HILL C. The HITRAN2016 molecular spectroscopic database[J]. Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy and Radiative Transfer, 2017, 203: 3-69. doi: 10.1016/j.jqsrt.2010.01.027 [16] 聂伟, 叶擎昊, 许振宇, 等. Voigt线型两翼拟合非均匀流场吸光度的方法研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2017, 37(3): 816-821. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2017)03-0816-06NIE W, YE Q H, XU Z Y, et al. Study on the method of Voigt profiles two wings fitting non-uniform flow field absorbance[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2017, 37(3): 816-821. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2017)03-0816-06 [17] 符鹏飞, 超星, 侯凌云, 等. 基于TDLAS技术的煤油燃烧温度与组分分布检测[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2019, 40(9): 2176-2182. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCRB201909033.htmFU P F, CHAO X, HOU L Y, et al. Measurement of kerosene combustion temperature and component distribution based on TDLAS technology[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2019, 40(9): 2176-2182. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCRB201909033.htm [18] ZHOU X, LIU X, JEFFRIES J B, et al. Development of a sensor for temperature and water concentration in combustion gases using a single tunable diode laser[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2003, 14(8): 1459-1468. doi: 10.1088/0957-0233/14/8/335 -








 下载:
下载: