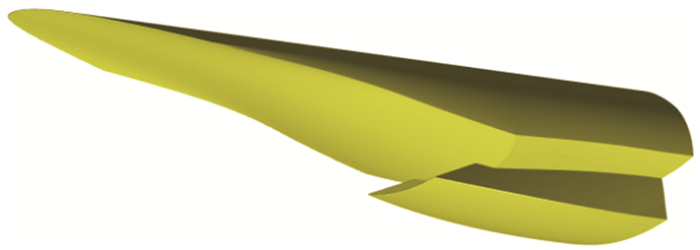
Experimental studies of Curved Cone Waverider forebody Inlet(CCWI) at low Mach number range
-
摘要: 为了研究新型一体化曲外锥乘波前体进气道在低马赫数端的自起动、抗反压特性及侧滑对性能的影响,基于几何约束及钝度修型的实用化风洞实验模型,采用进气道节流系统,在来流马赫数3.0、3.5和4.0,迎角-4°~6°范围内,不同堵锥位置状态下获得了一体化曲外锥乘波前体进气道的表面压力分布及流场高清纹影。实验结果表明,实验模型在来流马赫数3.5和4.0时具备自起动能力;在0°迎角,来流马赫数3.5和4.0,最大抗反压能力分别约为24和33倍来流压力;侧滑角对一体化曲外锥乘波前体进气道的流量捕获和流动压缩性能影响相对较弱。曲外锥乘波前体进气道具有同超燃冲压燃烧室、高超声速飞行器进行一体化设计的特性。Abstract: The self-start ability, anti-backpressure performance and side slip influences to the performance of the Curved Cone Waverider forebody Inlet(CCWI) were experimentally studied in the present paper. Based on the geometrically constrained and bluntly modified practical CCWI wind tunnel experimental model, using the inlet throttling systems, the static pressure distributions and high resolution sherilen maps of the CCWI's flow field were obtained at free steam Mach numbers(Ma∞) 3.0, 3.5 and 4.0 at different throttling cone positions. The experimental results show that the integrated CCWI model can self-start at Ma∞ 3.5 and 4.0. At the angle of attack 0°, its maximum anti-back pressure abilities is about 24 and 33 times of the free stream static pressure(p∞) at Ma∞ 3.5 and 4.0, respectively. Side slip has little influence on mass flow capture and flow compression abilities for CCWI. The study on CCWI can be used for practical integration studies with scramjet engine and air-breathing vehicles.
-
Key words:
- curved cone /
- waverider /
- inlet /
- self-start /
- anti-backpressure /
- experimental study
-
表 1 风洞自由来流条件
Table 1. Wind tunnel freestream flow conditions
Ma∞ p0/MPa T0/K Re 4.03 0.63 288 3.09 × 107 3.53 0.54 288 3.37× 107 3.01 0.36 288 2.91× 107 -
[1] Richard M, Scott M. X-51 development:a chief engineer's perspective[C]. 17th AIAA International Space Planes and Hypersonic Systems and Technologies Conference, 2011. [2] Kuchemann D. The aerodynamic design of aircraft[M]. Oxford:Pergamon Press, 1978:448-510. [3] Heiser W H, Pratt D T. Hypersonic airbreathing propulsion[M]. Published by American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics Inc, 1994:32-33. [4] Haney J W, Beaulieu W D. Wave rider inlet integration issues[R]. AIAA-1994-0383, 1994. [5] Vijay S, Andrew G, Mark S. Automated design optimization for the P2 and P8 hypersonic inlets[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 1997, 34(2):308-316. https://core.ac.uk/display/21977620 [6] Thomas M B, Norbert C B. Forebody precompression effects and inlet entry conditions for hypersonic vehicles[J]. Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets, 1998, 35(1):30-36. doi: 10.2514/3.26994 [7] Frederick S B, Robert A B, Tam C J. Design and analysis of streamline traced hypersonic inlets[R]. AIAA-1999-4974, 1999. doi: 10.2514/6.1999-4974 [8] Smart M K. Design of three-dimensional hypersonic inlets with rectangular to elliptical shape transition[J]. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 1999, 15(3):408-416. doi: 10.2514/2.5459 [9] O'Neill M K, Lewis M J. Optimized scramjet integration on a waverider[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 1992, 29(6):1114-1123. doi: 10.2514/3.56866 [10] Takashima N, Lewis M J. Engine-airframe integration on osculating cone waverider-based vehicle designs[R]. AIAA-96-2551, 1996. doi: 10.2514/6.1996-2551 [11] O'Brien T F, Lewis M J. Rocket-based combined-cycle engine integration on an osculating cone waverider vehicle[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2001, 38(6):1117-1123. doi: 10.2514/2.2880 [12] Sobieczky H, Dougherty F C, Jones K D. Hypersonic waverider design from given shock waves[C]//Proceedings of the First International Hypersonic Wave rider Symposium, University of Maryland, College Park, MD, 1990. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/225015124_Hypersonic_Waverider_Design_from_Given_Shock_Waves [13] Ryan P S, Mark J L. Design of an engine-airframe integrated hypersonic missile within fixed box constraints[R]. AIAA-99-0509, 1999. doi: 10.2514/6.1999-509 [14] You Y C, Zhu C X, Guo J L. Dual waverider concept for the integration of hypersonic inward-turning inlet and airframe forebody[R]. AIAA-2009-7421, 2009. doi: 10.2514/6.2009-7421 [15] Li Y Q, An P, Pan C J, et al. Integration methodology for waverider-derived hypersonic inlet and vehicle forebody[R]. AIAA-2014-3229, 2014. doi: 10.2514/6.2014-3229 [16] 贺旭照, 周正, 倪鸿礼.密切内锥乘波前体进气道一体化设计和性能分析[J].推进技术, 2012, 33(4):510-515. http://www.oalib.com/paper/5111622He X Z, Zhou Z, Ni H L. Integrated design methods and performance analyses of osculating inward turning cone waverider forebody inlet(OICWI)[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 2012, 33(4):510-515. http://www.oalib.com/paper/5111622 [17] He X Z, Le J L, Zhou Z, et al. Osculating inward turning cone waverider/inlet (OICWI) design methods and experimental study[R]. AIAA-2012-5810, 2012. doi: 10.2514/6.2012-5810?mi=8fbwx6&af=R&contents=articlesChapters&countTerms=true&field1=Contrib&target=default&text1=xuzhao%2C+h [18] 周正, 贺旭照, 卫锋, 等.密切曲内锥乘波前体进气道低马赫数性能实验研究[J].推进技术, 2016, 37(8):1455-1460. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=tjjs201608007&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQZhou Z, He X Z, Wei F, et al. Experimental studies of osculating inward turning cone waverider forebody inlet(OICWI) at low Mach number conditions[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 2016, 37(8):1455-1460. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=tjjs201608007&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [19] 贺旭照, 乐嘉陵.曲外锥乘波体进气道实用构型设计和性能分析[J].航空学报, 2016, DOI: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2016.0289.He X Z, Le J L. Design and performances analysis of a practical curved cone waverider inlet[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2016, DOI: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2016.0289. [20] He X Z, Le J L, Wu Y C. Design of a curved cone derived waverider forebody[R]. AIAA-2009-7423, 2009. doi: 10.2514/6.2009-7423 [21] 贺旭照, 倪鸿礼.密切曲面锥乘波体-设计方法和性能分析[J].力学学报, 2011, 43(6):1077-1082. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-2011-6-lxxb2010-502He X Z, Ni H L. Osculating curved cone(OCC) waverider:Design method and performance analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2011, 43(6):1077-1082. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-2011-6-lxxb2010-502 [22] Trent T, David Van W. Performance analysis of hypersonic shape changing inlets derived from morphing streamline traced flowpaths[R]. AIAA-2008-2635, 2008. doi: 10.2514/6.2008-2635 [23] http://www.cardc.cn:88/html/Facility/f2/65.html [24] He X Z, Zhao H Y, Le J L. Application of wall function boundary condition considering heat transfer and compressibility[J]. Acta Aerodynamic Sinica, 2006, 24(4):450-453. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/293761189_Application_of_wall_function_boundary_condition_considering_heat_transfer_and_compressibility [25] Simon T, Philippe D, Sébastien D. Experimental study of supersonic inlet buzz[J]. AIAA Journal, 2006, 44(10):2354-2365. doi: 10.2514/1.20451 -








 下载:
下载: