Study on three dimensional laser-induced fluorescence (3DLIF) techniques and its instrument
-
摘要: 本文介绍了激光诱导荧光(LIF)技术测量水体浓度场、温度场和速度场的基本原理,总结了从一维到三维LIF技术的发展历程,综述了激光诱导荧光(LIF)技术测量水体标量场的关键问题,包括激光器和片光源、荧光物质选择和校正方法,从工程化和产业化的需求出发,提出了基于3DLIF技术的水体三维标量场测量仪器的总体技术方案、技术路线和总体技术指标,并给出了3DLIF的关键技术及其解决方案。
-
关键词:
- 三维激光诱导荧光技术(3DLIF) /
- 水体 /
- 标量场测量
Abstract: This paper introduces the principle of the LIF technique to measure the water concentration, temperature and velocity fields, summarizes the LIF technology development from 1D to 3D, reviews the key issues of LIF to measure the scalar field in water, including laser and light-sheet sources, fluorescence material selections and calibration methods, and finally reviews various correction methods of PLIF and 3DLIF. Based on the 3DLIF techniques, this paper proposes an overall technical scheme, technical route and overall technical indicators of 3DLIF instrument, and then provides solutions of 3DLIF key techniques to meet the demand of engineering and industrialization. -
图 1 荧光素钠溶液谱图[1]
Figure 1. Fluorescent sodium solution spectra
图 3 液体中荧光素钠的荧光强度随浓度变化[1]
Figure 3. The variance of the fluorescence intensity with fluorescent sodium concentration in the liquid
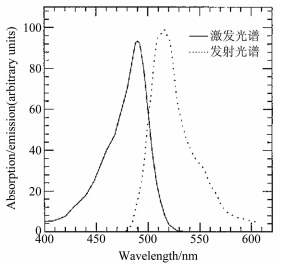
图 4 不同温度条件下罗丹明B的激发-发射光谱[3]
Figure 4. The excitation-emission spectrums of rhodamine B under different temperature conditions
图 5 罗丹明B的荧光强度随温度线性变化[3]
Figure 5. Linear change of rhodamine B fluorescence intensity with temperature
图 7 扇形片光源系统示意图[10]
Figure 7. Schematic of fan-type laser-sheet
图 8 3种片光源扫描系统[15]
Figure 8. Three light-scanning systems
图 9 双振镜3DLIF测量示意[10]
Figure 9. Schematic of 3DLIF measurement with double vibrating mirrors
表 1 3种常见荧光物质的适宜激发波长
Table 1. Matched excitation wavelengths of three common fluorescent materials
荧光物质 激发谱波长/nm[21] 适宜激光波长/nm 测量参量 最小 最大 峰值 荧光素钠 430 520 490 460~500 浓度 罗丹明6G 460 560 530 500~550 浓度 罗丹明B 460 590 550 525~575 温度 表 2 新型荧光物质
Table 2. New fluorescent materials
序号 荧光物质名称 文献 1 Carboxy-seminapthorhodafluoror SNARF [22] 2 Seminaphthofluoresceinor SNAFL 3 1,4-Dihydroxyphthalonitrile(DHPN) 4 Hydroxypyrene-1,3,6 trisulfonic acid (HPTS) 5 Lucifer yellow 6 Phloxine B 7 Kiton red 8 LDS 698(or pyridine 1) 9 Rhodamine系列:Rhodamine B,Rhodamine 6G,Rhodamine WT,Rhodamine 610,Rhodamine110,Sulforhodamine 640 10 5(6)-Carboxy-2′, 7′-dichlorofluorescein [1] 11 Pyrromethene 556 [23] 12 Alexa dyes(Alexa 350,Alexa 430,Alexa 488,Alexa 532,Alexa 546,Alexa 568,and Alexa 594 dyes) [24] 表 3 仪器总体技术指标
Table 3. Overall technical indicators of 3DLIF equipment
技术指标 精度或范围 三维测量范围 (0.3~0.5) m×1m×1m 测量精度 < 10-2ppm(浓度场); < 0.2℃(温度场) 最大扫描速度 1m/s 图像分辨率 1280pixel×1024pixel 满分辨率帧速 500帧/s -
[1] Karasso P S, Mungal M G. PLIF measurements in aqueous flows using the Nd:YAG laser[J]. Experiments in Fluids, 1997, 23(5):382-387. doi: 10.1007/s003480050125 [2] 陈国珍.荧光分析法[M].北京:科学出版社, 1990.Chen G Z. Fluorescence analysis[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 1990. [3] 杜闰萍, 刘喆, 程易, 等.平面激光诱导荧光技术用于快速液-液混合过程温度场测量[J].过程工程学报, 2007, 7(5):859-864. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGYJ200705004.htmDu R P, Liu Z, Cheng Y, et al. Planar laser induced fluorescence technique for rapid liquid-liquid mixing process temperature field measurement[J]. Journal of Process Engineering, 2007, 7(5):859-864. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGYJ200705004.htm [4] 申功炘, 晋健. LIF喷流混合流浓度场定量测量[J].力学学报, 1992, 24(4):488-492. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LXXB199204012.htmShen G X, Jin J. LIF jet mixing flow concentration field quantitative measurement[J]. Journal of Mechanics, 1992, 24(4):488-492. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LXXB199204012.htm [5] 黄真理, 李玉梁, 余常昭. PLIF技术测量浓度场及其二维数字校正[J].力学学报, 1994, 26(5):616-624. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LXXB405.012.htmHuang Z L, Li Y L, Yu C Z. PLIF technique to measure the concentration field and the two-dimensional digital correction[J]. Journal of Mechanics, 1994, 26(5):616-624. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LXXB405.012.htm [6] 黄真理, 李玉梁, 余常昭.平面激光诱导荧光技术测量横流中射流浓度场的研究[J].水利学报, 1994, (11):1-7. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0559-9350.1994.11.001Huang Z L, Li Y L, Yu C Z. Planar laser induced fluorescence technique measure transverse jet concentration field in the study[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 1994, (11):1-7. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0559-9350.1994.11.001 [7] Prasad R R, Sreenivasan K R. Quantitative three-dimensional imaging and the structure of passive scalar fields in fully turbulent flows[J]. J Fluid Mech, 1990, 216:1-34. doi: 10.1017/S0022112090000325 [8] Dahm W J A, Southerland K B, Buch K A. Direct, high resolution, four-dimensional measurements of the fine scale structure of Sc》1 molecular mixing in turbulent flows[J]. Physics of Fluids A, 1991, 3(5):1115-1127. doi: 10.1063/1.858093 [9] Deusch S, Dracos T. Time resolved 3D passive scalarconcentration-field imaging by laser induced fluorescence(LIF)in moving liquids[J]. Meas Sci Technol, 2001, 12(2):188-200. doi: 10.1088/0957-0233/12/2/310 [10] Tian X D, Roberts P J W. A 3D LIF system for turbulent buoyant jet flows[J]. Experiments in Fluids, 2003, 35(6):636-647. doi: 10.1007/s00348-003-0714-x [11] Van Vliet E, Van Bergen S M, Derksen J J, et al. Time-resolved, 3D, laser-induced fluorescence measurements of fine-structure passive scalar mixing in atubular reactor[J]. Experiments in Fluids, 2004, 37(1):1-21. doi: 10.1007/s00348-004-0779-1 [12] Delo C J, Kelso R M, Smits A J. Three-dimensional structure of a low-Reynolds-number turbulent boundary layer[J]. J Fluid Mech, 2004, 512:47-83. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Richard_Kelso/publication/231965363_Three-dimensional_structure_of_a_low-Reynolds-number_turbulent_boundary_layer/links/54202eed0cf241a65a1b0d6f.pdf?inViewer=true&pdfJsDownload=true&disableCoverPage=true&origin=publication_detail [13] Sarathi P. A calibration scheme for quantitative concentration measurements using simultaneous PIV and 3DLIF[J]. Experiments in Fluids, 2012, 52:247-259. Doi: 10.1007/s00348-011-1219-7. [14] Dahm W J A, Su L K, Southerland K B. A scalar imaging velocimetry technique for fully resolved four-dimensional vector velocity field measurements in turbulent flows[J]. Physics of Fluids A, 1992, 4(10):2191-2206. doi: 10.1063/1.858461 [15] Crimaldi J P. Planar laser induced fluorescence in aqueous flows[J]. Experiments in Fluids, 2008, 44:851-863. Doi: 10.1007/s00348-008-0496-2. [16] Koga D J, Abrahamson S D, Eaton J K. Development of a portable laser sheet[J]. Experiments in Fluids, 1987, 5:215-216. doi: 10.1007/BF00298466 [17] 唐静, 谢正茂, 何俊华, 等.用于尾流探测的新型片光源[J].光电子·激光, 2012, 23(2):408-412. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDZJ201202037.htmTang J, Xie Z M, He J H, et al. New light source to detect wake flow[J]. Journal of Optoelectronics, Lasers, 2012, 23(2):408-412. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDZJ201202037.htm [18] 唐洪武.现代流动测试技术及应用[M].北京:科学出版社, 2009.Tang H W. Modern flow measurement technology and application[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 2009. [19] 夏国朝, 陶慧林.罗丹明6G的三维荧光和共振散射光谱[J].光谱实验室, 2008, 25(5):773-777. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GPSS200805002.htmXia G C, Tao H L. Three-dimensional fluorescence and resonance scattering spectral of rhodamine 6G[J]. Journal of Spectroscopy Laboratory, 2008, 25(5):773-777. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GPSS200805002.htm [20] Sakakibara J, Hishida K, Maeda M. Measurements of thermally stratified pipe flow using image-processing techniques[J]. Experiments in Fluids, 1993, 16:82-96. doi: 10.1007/BF00944910 [21] Arcoumanis C, McGuirk J J, Palma J M L. On the use of fluorescent dyes for concentration measurements in water flows[J]. Experiments in Fluids, 1990, 10:177-180. doi: 10.1007/BF00215028 [22] Coppeta J, Rogers C. Dual emission laser induced fluorescence for direct planar scalar behavior measurements[J]. Experiments in Fluids, 1998, 25:1-15. doi: 10.1007/s003480050202 [23] Cowen E A, Chang K A, Liao Q. A single-camera coupled PTV-LIF technique[J]. Experiments in Fluids, 2001, 31:63-73. doi: 10.1007/s003480000259 [24] Nataliya P V, Rosaria P H, Janell B S, et al. Alexa dyes, a series of new fluorescent dyes that yield exceptionally bright, photostable conjugates[J]. J Histochem Cytochem, 1999, 47(9):1179-1188. doi: 10.1177/002215549904700910 [25] Sakakibara J, Adrian R. Whole field measurement of temperature in water using two-color laser-induced fluorescence[J]. Experiments in Fluids, 1999, 26:7-15. doi: 10.1007/s003480050260 [26] Hishida K, Sakakibara J. Combined planar laser-induced fluorescence and particle image velocimetry technique for velocity and temperature fields[J]. Experiments in Fluids, 2000, 29:S129-S140. doi: 10.1007/s003480070015 [27] Kim K S, Choi M S, Lee C H, et al. In-cylinder fuel distribution measurements using PLIF in a SI engine[C]. SAE Special Publications, Detroit, MI, USA, 1997. [28] Matthias B, Fabrice G, Fabrice L. Instant aneous measurement of two-dimensional temperature distributions by means of two-color planar laser induced fluorescence (PLIF)[J]. Experiments in Fluids, 2005, 38:123-131. Doi: 10.1007/s00348-004-0911-2. [29] Kaiser S A, Long M B. Quantitative planar laser-induced fluorescence of naphthalenes as fuel tracers[J]. Proc of the Combustion Institute, 2005, 30:1555-1563. doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2004.08.263 [30] 黄真理, 李玉梁, 余常昭, 等. LIF技术测量浓度场的影响因素分析[J].实验力学, 1994, 9(3):232-240. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYLX403.007.htmHuang Z L, Li Y L, Yu C Z, et al. Factors influencing the concentration field of LIF technology measurement[J]. Journal of Experimental Mechanics, 1994, 9(3):232-240. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYLX403.007.htm -








 下载:
下载: