Velocity measurements for flows around micro-cylinder array based on image overlapping
-
摘要: 分析了相关深度对Micro-PIV速度场测量的影响,说明采用低密度粒子图像叠加技术能够有效减小相关深度,提高速度测量的准确性。将该方法应用于微柱群绕流流场的分层测量,雷诺数分别取0.8~3.6,在此基础上计算了空间平均速度。将分层速度场和平均速度廓线与采用平均相关技术获得的结果进行了比较。结果表明,采用低密度粒子图像叠加方法获得的全场绕流速度分布更为合理,通道底部和顶部近壁区的平均“伪滑移速度”分别减小了22.7%和17.2%,通道中心平均速度峰值增加了5.2%。
-
关键词:
- 显微粒子图像测速技术 /
- 图像叠加法 /
- 微柱群绕流 /
- 分层测量
Abstract: In this study, the influence of depth of correlation (DOC) on the micro-PIV measurement is analyzed. The method of image overlapping under the low particle density condition can decrease DOC and improve the velocity measurement accuracy. This method is applied to the velocity measurements on multiple fluid planes for the flow around a micro-cylinder array under eight Reynolds numbers from 0.8 to 3.6, and the spatial averaged velocities (SAVs) are calculated based on the velocities. In order to analyze the measurement accuracy, the velocities and SAVs resulting from the method of image overlapping are compared to those obtained by the method of average cross-correlation. The results indicate that of the image overlapping is a more reasonable method under the low particle density condition. The average pseudo-slip velocity decreases by 22.7% for the bottom surface and 17.2% for the top, respectively, and the average peak velocity increases by about 5.2%. -
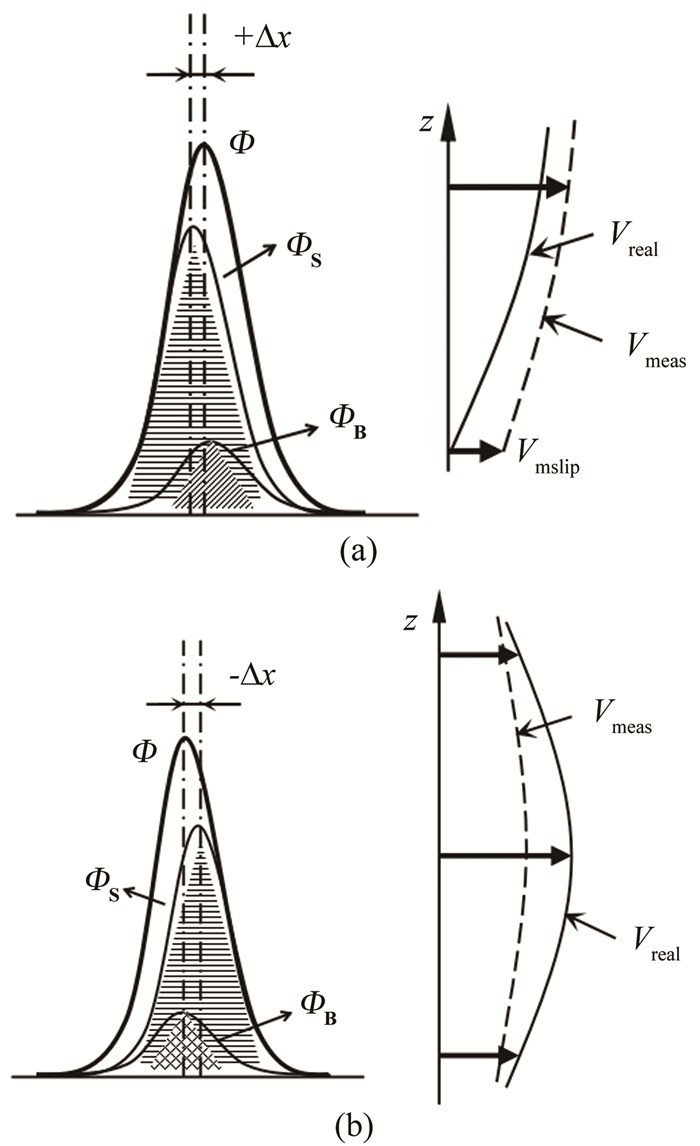
图 1 相关深度对相关函数的影响示意图。(a)近壁区相关峰值的正偏差,出现“伪滑移速度”; (b)中心层平面相关峰值的负偏差。图中±Δx为位移偏差; Φ, ΦS及ΦB分别为总相关函数, 焦平面粒子及背景粒子图像对相关函数的贡献; Vmeas及Vreal分别为速度测量值和真实值。
Figure 1. The influence of DOC on the correlation function. (a) Positive deviation of correlation peak near wall surface, "pseudo-slip flow"; (b) Negative deviation of correlation peak on center plane. where±Δx is the displacement deviation; Φ, ΦS and ΦB are the total correlation function and correlation function contributed by in-plane particle images and background particle images, respectively; Vmeas and Vreal are the measurement value and real value of velocity, respectively.
表 1 2种方法的壁面速度
Table 1. Velocities on two walls by two methods
Re 0.8 1.2 1.6 2.0 2.4 2.8 3.2 3.6 平均值 Q/(μl·s-1) 14.3 21.5 28.6 35.8 42.9 50.1 57.2 64.4 / 底面VS, a/(mm·s-1) 8.6 14.7 18.7 20.5 27.3 25.6 36.0 37.1 / 底面VNDS, a 0.43 0.49 0.47 0.41 0.46 0.37 0.45 0.41 0.44 底面VS, o/(mm·s-1) 5.4 11.5 12.5 18.4 21.2 17.6 30.4 33.5 / 底面VNDS, o 0.27 0.38 0.31 0.37 0.36 0.25 0.38 0.37 0.34 底面δS/% -37.2 -21.8 -33.2 -10.2 -22.3 -31.3 -15.6 -9.7 -22.7 顶面VS, a/(mm·s-1) 10.6 12.3 12.6 21.9 21.3 28.9 29.5 37.6 / 顶面VNDS, a 0.53 0.41 0.32 0.44 0.36 0.41 0.37 0.42 0.41 顶面VS, o/(mm·s-1) 9.1 10.7 13.5 16.3 13.8 20.5 23.2 35.1 / 顶面VNDS, o 0.46 0.36 0.34 0.33 0.23 0.29 0.29 0.39 0.34 顶面δS/% -14.2 -13.0 7.1 -25.6 -35.2 -29.1 -21.4 -6.6 -17.2 表 2 2种方法的峰值速度
Table 2. Peak velocities by two methods
Re 0.8 1.2 1.6 2.0 2.4 2.8 3.2 3.6 平均值 Q/(μl·s-1) 14.3 21.5 28.6 35.8 42.9 50.1 57.2 64.4 / VP, a/(mm·s-1) 24.2 31.7 46.3 54.1 66.3 75.3 89.5 98.2 / VNDP, a 1.22 1.06 1.16 1.09 1.11 1.08 1.12 1.10 1.12 VP, o/(mm·s-1) 24.7 35 45.8 58.7 72.2 78.9 93.8 101.3 / VNDP, o 1.24 1.17 1.15 1.18 1.21 1.13 1.18 1.13 1.17 δS/% 2.1 10 -1.1 8.5 8.9 4.8 4.8 3.2 5.2 -
[1] Yoshida H. The wide variety of possible applications of micro-thermofluid control[J]. Microfluid Nanofluid, 2005, 1:289-300. doi: 10.1007/s10404-004-0014-7 [2] Yeom J, Agonafer D D, Han J H, et al. Low Reynolds number flow across an array of cylindrical microposts in a microchannel and figure-of-merit analysis of micropost-filled microreactors[J]. J Micromech Microeng, 2009, 19:065025. doi: 10.1088/0960-1317/19/6/065025 [3] Tamayol A, Khosla A, Gray, et al. Bahrami creeping flow through ordered arrays of micro-cylinders embedded in a rectangular minichannel[J]. Int J Heat Mass Transfer, 2012, 55(15-16):3900-3908. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2012.03.008 [4] Wang D M, Tarbell J M. Modeling interstitial flow in an artery wall allows estimation of wall shear stress on smooth muscle cells[J]. J Biomech Eng, 1995, 117:358-363. doi: 10.1115/1.2794192 [5] Tada S, Tarbell J M. Interstitial flow through the internal elastic lamina affects shear stress on arterial smooth muscle cells[J]. Amercian Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory, 2000, 278:1589-1597. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/12541875_Interstitial_flow_through_the_internal_elastic_lamina_affects_shear_stress_on_arterial_smooth_muscle_cells [6] Nagrath S, Sequist L V, Maheswaran S, et al. Isolation of rare circulating tumour cells in cancer patients by microchip technology[J]. Nature, 2007, 450:1235-1239. doi: 10.1038/nature06385 [7] Santiago J G, Wereley S T, Meinhart C D. A particle image velocimetry system for microfluidics[J]. Exp Fluids, 1998, 25(4):316-319. doi: 10.1007/s003480050235 [8] Wereley S T, Meinhart C D. Recent advances in micro-particle image velocimetry[J]. Annu Rev Fluid Mech, 2010, 42:557-576. doi: 10.1146/annurev-fluid-121108-145427 [9] Wereley S T, Meinhart C D, Gray M H B. Depth effects in volume illuminated particle image velocimetry[C]. The Third International Workshop on Particle Image Velocimetry, Santa Barbara, 1999:545-550. [10] Olsen M G, Adrian R J. Out-of-focus effects on particle image visibility and correlation in microscopic particle image velocimetry[J]. Exp Fluids, 2000, 29:S166-S174. doi: 10.1007/s003480070018 [11] Chuong V, Nguyen A F, Josie C. Improvement of measurement accuracy in micro PIV by image overlapping[J]. Exp Fluids, 2010, 49:701-712. doi: 10.1007/s00348-010-0837-9 [12] Wereley S T, Gui L, Meinhart C D. Advanced algorithms for microscale particle image velocimetry[J]. AIAA J, 2002, 40:1047-1055. doi: 10.2514/2.1786 [13] Massimiliano R, Rodrigo S, Christian C, et al. On the effect of particle image intensity and image preprocessing on the depth of correlation in micro-PIV[J]. Exp Fluids, 2012, 52:1063-1075. doi: 10.1007/s00348-011-1194-z [14] 王昊利, 王元. Micro-PIV--粒子图像测速技术的新进展[J].力学进展, 2005, 35(1):77-90. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LXJZ200501008.htmWang H L, Wang Y. Micro-PIV--the new trend of Particle Image Velocimetry[J]. Advance in Mechanics, 2005, 35(1):77-90. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LXJZ200501008.htm [15] Nam-Trung N, Steven T, Wereley S T. Fundamentals and applications of microfluidics[M]. Artech House, Inc, 2002. [16] 徐明, 王昊利.基于低密度粒子图像叠加的Micro-PIV速度场测量[J].实验流体力学, 2013, 27(2):106-112. http://www.syltlx.com/CN/abstract/abstract10342.shtmlXu M, Wang H L. The micro-PIV measurement based on the low particle density[J]. Journal of Experiments in Fluid Mechanics, 2013, 27(2):106-112. http://www.syltlx.com/CN/abstract/abstract10342.shtml [17] Bitsch L, Olesen L, Westergaard C, et al. Micro particle-image velocimetry of bead suspensions and blood flows[J]. Exp Fluids, 2005, 39:507-513. doi: 10.1007/s00348-005-0967-7 -








 下载:
下载: